
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski The Fraud Scoring System is an anti-fraud tool used in the IT industry to evaluate the likelihood of fraudulent or deceptive behavior in various online activities, including financial transactions, e-commerce, and online payments. This system is essential in areas where fraud protection and customer reliability are crucial.
The term “FraudScore” is also commonly used in relation to IP addresses. Many online services claim to assess the “FraudScore” of an IP address, purporting to check for potential fraudulent activities associated with it. This is particularly relevant for users interested in the credibility of an IP address, such as after purchasing a proxy. However, these online checkers are not related to the Fraud Scoring System and generally do not provide accurate or relevant information.
In the following sections, we will explore the concept of an IP address's Fraud Score, discuss its reliability, and guide you on how to evaluate the trustworthiness of your own or a purchased IP address.
The significance of fraudster identification systems is paramount in ensuring online security. However, the value of assessing the fraud risk of IP addresses is debatable and tends to be minimal. This skepticism is due to several factors:
Given these shortcomings, the reliability of such checkers in detecting IP address fraud is questionable. Therefore, relying on public resources for evaluating your own or a purchased IP address is not recommended.
A more effective approach involves assessing other indicators of an IP address, such as its presence on blacklists/spam lists and its anonymity level.
Various IP checkers offer comprehensive analysis, providing information about:
Ultimately, the purpose of these IP checkers is to enhance online security and safeguard users against potential threats.
Exploring operational methods for IP checking, we focus on specialized online services. As previously discussed, relying solely on Fraud Score is not reliable. Instead, let's consider other important indicators obtained during IP checks.
To begin, here's how to gather general information about your IP:
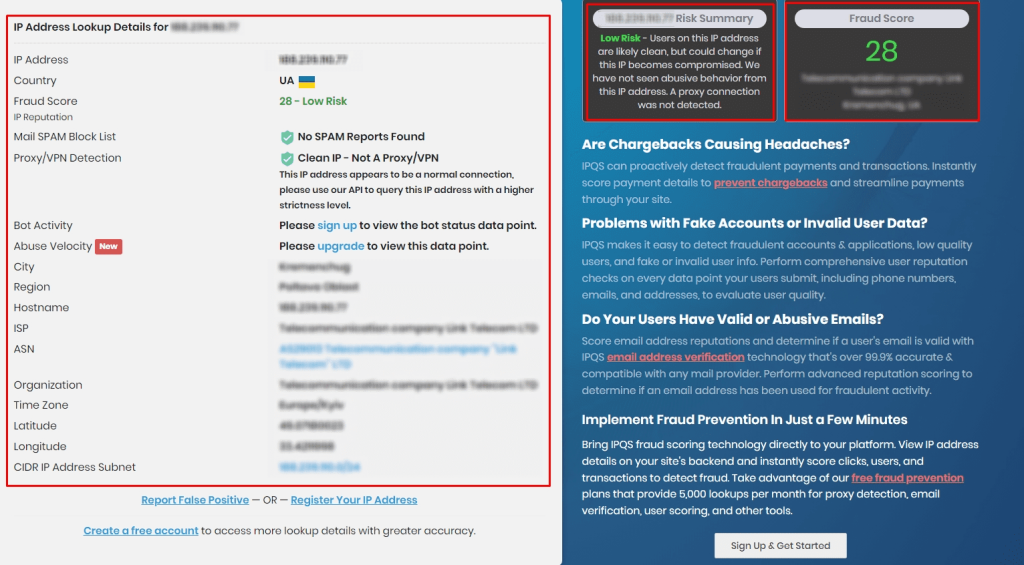
For a more comprehensive evaluation, it’s advisable to cross-reference IPs using separate blacklist checkers. This approach ensures a more thorough assessment of the IP's reliability.
Let's take the DNS Checker service as an example, which analyzes data from over 50 databases. Here's how to use it:
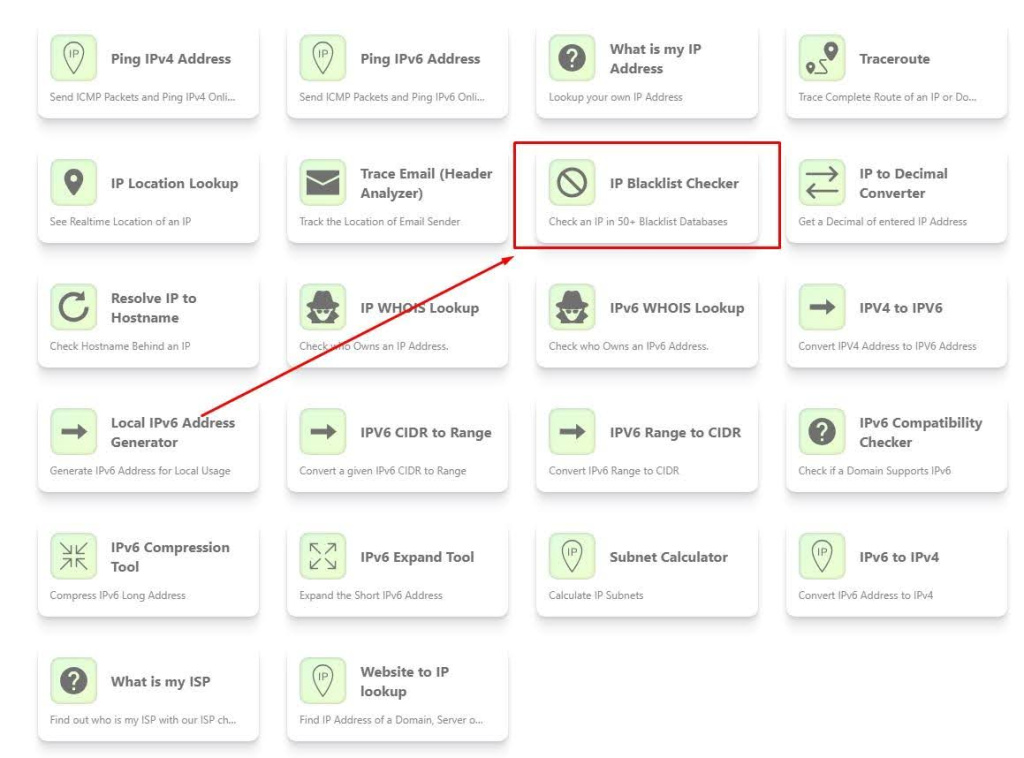
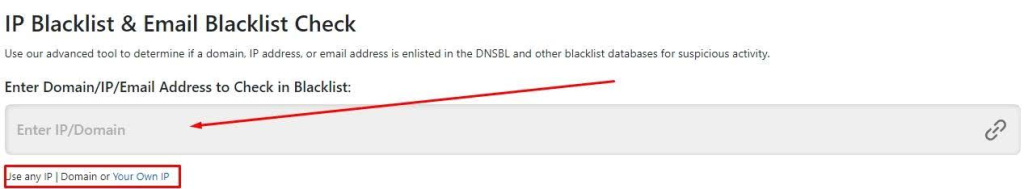
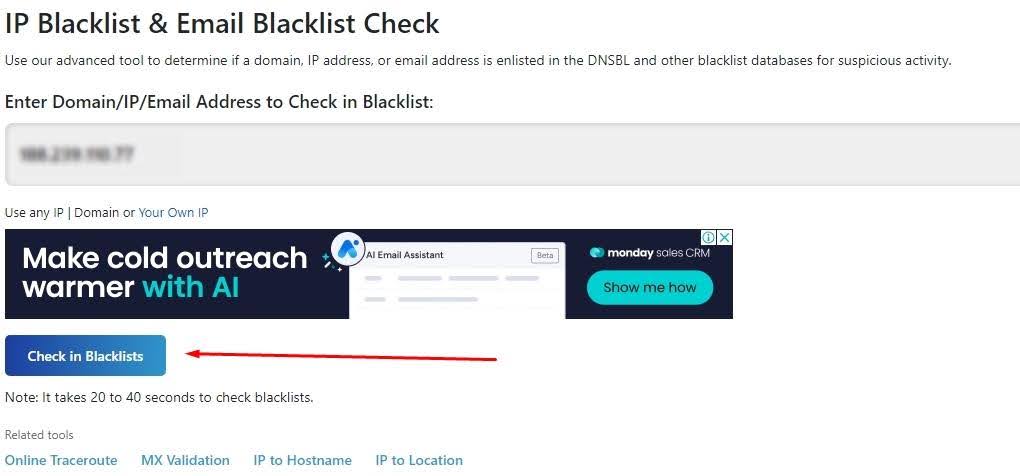
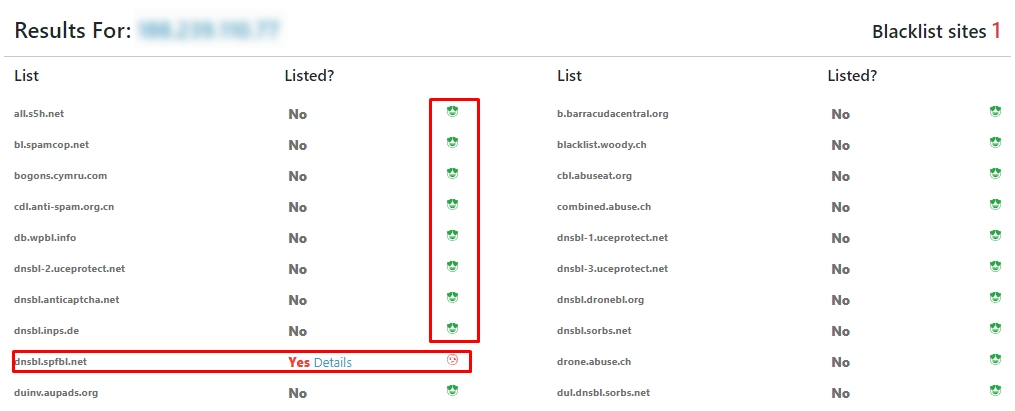
It's important to note that an IP’s presence in one database doesn’t necessarily imply unreliability. However, if the IP appears on multiple blacklists, it's generally advised not to use it.
Checking your IP for anonymity is also crucial, as it reveals how other sites perceive your online identity and whether sensitive user information is visible. Since an IP address can contain data that's not only useful for web service analytics but also vulnerable to attackers, it's important to understand what your IP reveals.
Here's how to conduct an anonymity check using the 2ip checker:

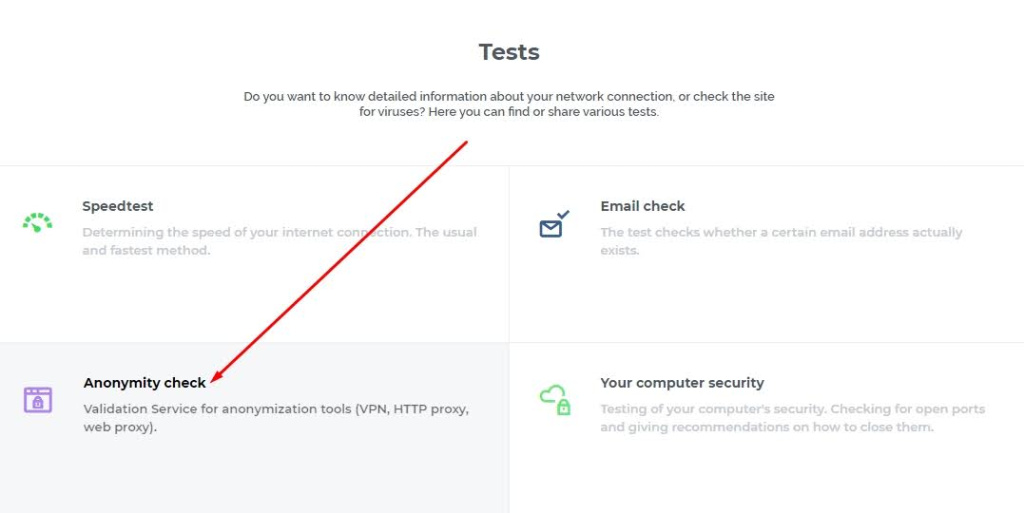
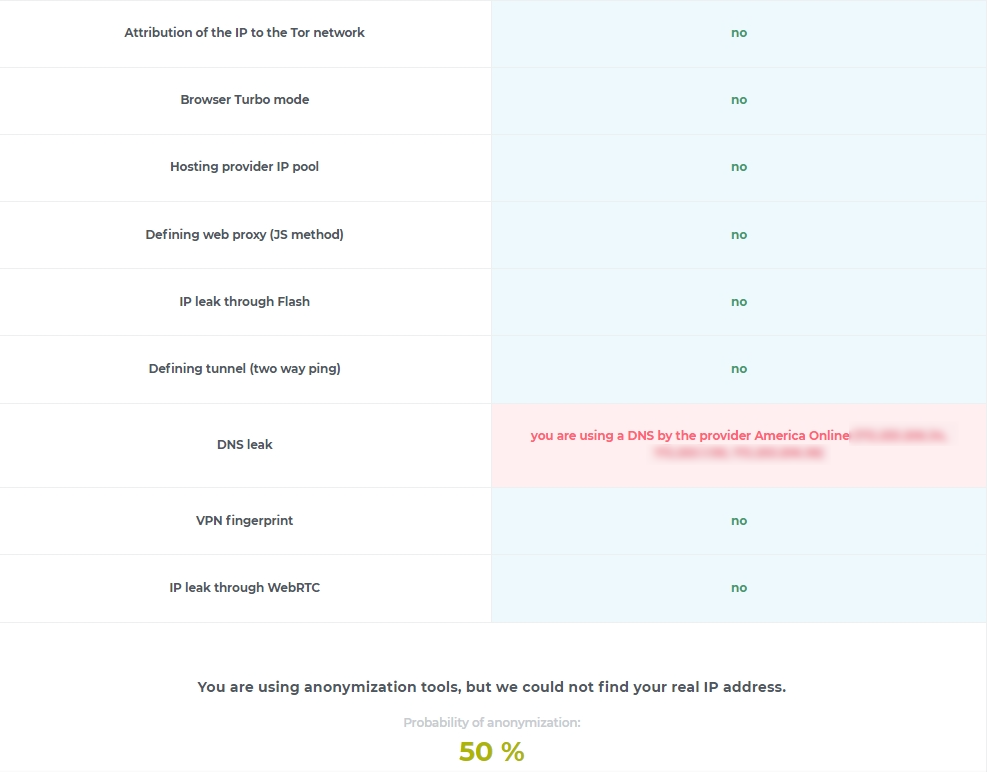
This check helps assess how “clean” and safe your IP is for use (more about “clean proxies”). However, keep in mind that results from online IP checkers may vary and might not be entirely comprehensive, depending on the service used.
Traditional rules-based FraudScore systems have apparent limitations. They rely on fixed rules that can be inflexible and easy for fraudsters to bypass. These systems often produce high rates of false positives, flagging legitimate activities as fraudulent. They also miss important context and patterns that don’t fit preset criteria.
AI and machine learning (ML) overcome these limits by learning from data and adapting over time. Instead of static rules, AI/ML models identify complex and new fraud patterns instantly. They use supervised learning from labeled fraud cases, unsupervised learning for anomaly detection, and reinforcement learning to improve decision-making continuously.
Key benefits of AI/ML in FraudScore systems include:
You’ll also benefit from “whitebox” systems that provide explainable decisions through explainable AI (XAI) tools like LIME and SHAP. These solutions make AI’s FraudScore decisions transparent, helping you trust and refine the system.
In contrast to rigid rules, AI/ML models learn continuously and generate features automatically from data, making fraud detection smarter and more agile. Harnessing network intelligence is essential – it enriches FraudScore analytics and helps stop synthetic fraud attacks by spotting links between entities that rules miss.
Implementing a successful FraudScore solution requires a comprehensive, practical strategy. You’ll want to:
Tools and approaches to support these best practices include:
Here’s a practical checklist to get started:
By following these best practices, you’ll build a robust FraudScore system that evolves with threats and efficiently safeguards your business.
While FraudScore systems grow smarter, challenges remain. One major issue is inconsistent scoring thresholds across companies. This inconsistency causes interoperability problems when sharing fraud data or insights. Static, outdated models quickly lose effectiveness against rapidly changing fraud methods.
Inaccurate FraudScore results may lead to false positives that erode customer trust or false negatives that result in losses. The quality and completeness of your data play a huge role – missing or noisy data weakens model performance. Finally, regulatory demands and ethical concerns require transparency and fairness in automated decisions.
| Challenge or Limitation | How to Fix |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent scoring thresholds | Update models regularly and monitor performance continuously using tools like DataRobot or Databricks. |
| Static, outdated models | |
| Inaccurate FraudScore results | Ensure accurate, integrated data from various sources (CRM systems, device telemetry, external threat intelligence feeds such as IBM X-Force and VirusTotal). |
| Poor data quality/completeness | |
| Regulatory demands & ethical concerns | Implement bias detection and mitigation to maintain fairness and avoid discriminatory effects in scoring. |
Managing these factors protects your FraudScore system’s reliability and reputation while complying with regulations.
Integrating Proxy-Seller proxies is a practical checklist item to enhance FraudScore accuracy by providing secure, high-speed internet access for data collection and verification steps.
a broad selection of proxies – including residential, ISP, datacenter IPv6, IPv4 mix, and mobile proxies – allowing you to tailor your fraud detection to location targeting, IP rotation, and anonymity needs. Its 24/7 support, easy API integration, high uptime, flexible billing, and user-friendly control panel simplify management.
Using Proxy-Seller proxies helps your fraud detection teams reliably validate suspicious activities by accessing diverse IP addresses and geographic locations. This reduces false positives caused by IP-related anomalies and makes sure consistent data collection and testing environments are used. Consequently, your AI/ML models become more accurate, detecting fraud patterns faster while preserving privacy and complying with regulations.
Comments: 0