
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski A proxy server forwards requests between your device and the internet, helping mask the IP address, improve security, and manage traffic. For API testing, such intermediaries are important because they allow developers to simulate conditions, bypass restrictions, and keep requests anonymous. Properly configured Postman proxy settings ensure consistent and secure API testing. The service is widely used for building and testing APIs, and configuring a new connection ensures control over routing, filtering, and authentication. This guide explains step-by-step how to set up an intermediary in Postman for reliable results.
The setup process is straightforward, but accuracy is important. Each part of the configuration must be entered correctly. Otherwise, requests may fail or bypass it entirely.
The following steps explain the process in detail, from renting a private IP to saving the configuration inside the Postman application. Following them ensures that your Postman proxy settings work as intended.
The first step is to obtain access to reliable IPs. Free solutions are often tempting, but they come with serious drawbacks: limited speed, frequent downtime, and shared usage with many people. Because they are public, they are also more likely to be blocked by websites or flagged for suspicious activity.
When selecting it, ensure it supports the HTTP or HTTPS protocols. Postman does not support SOCKS proxy, which means SOCKS-based IPs cannot be used. Look for providers that offer private access, a stable connection, and fast speeds.
Select “Settings”. This option brings up the main configuration window where all preferences can be adjusted. Settings in Postman are divided into tabs, including General, Themes, Shortcuts, and Proxy. The last tab is the one required for this setup.
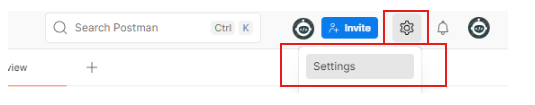
Inside the Settings window, click on the “Proxy” tab. Here you will see options to enable or disable usage, select type, and input other details.
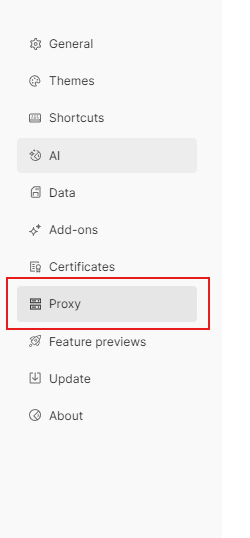
To begin, switch the toggle to the “On” position. This activates new IP use for all future requests.
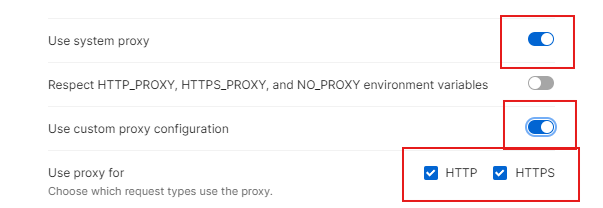
Next, select the type you are connecting to, typically HTTP or HTTPS.
Enter the IP address and port number into the appropriate fields. These details should be provided by your provider when you rent the new IP.
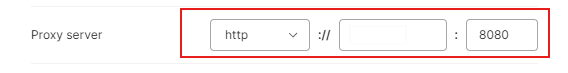
This stage represents the core of how to use proxy in Postman, since the server details determine whether requests are routed properly. A mistake in the IP address or port will result in failed connections or unprotected traffic. Careful entry here is therefore essential.
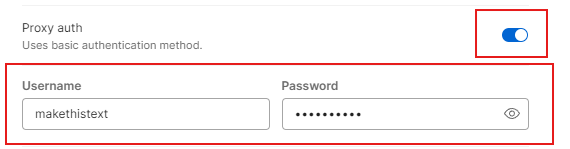
Some providers require authentication. This means you must log in with a username and password before using the service. In Postman, this is managed through the Proxy tab.
Turn the toggle for “Proxy Auth” to the “On” position. Then enter the username and password provided by your service.
Authentication secures access to the intermediary server by requiring valid credentials. For those who manage sensitive requests, enabling this option helps prevent misuse and ensures only approved users are able to apply the configured Postman proxy settings.
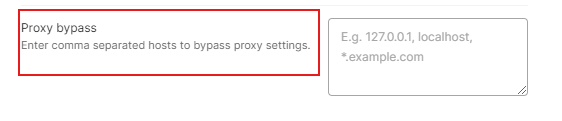
In some cases, you may want specific sites or requests to avoid using the server. For example, local development environments or trusted internal resources may not require routing. In Postman, this can be managed with the Proxy Bypass option.
In the same tab, find the field labeled “Proxy Bypass”. Enter the list of domains that should be excluded from the server. Separate them with commas if there are multiple entries. Any requests to these domains will bypass it and connect directly.
After entering all required details, click the close button in the settings window. Changes are saved automatically in Postman, so there is no separate “Save” option. Closing the window completes the configuration process. From this point forward, requests in Postman will be routed according to the defined settings.
To configure the Postman proxy with your system settings, open Postman and go to Settings, then click Proxy. Enable the “Use System Proxy” toggle. This routes your HTTP(S) requests through your operating system’s proxy configuration.
OS Configuration:
Make sure these OS settings are active before enabling system proxy in Postman.
Authentication and Best Practices:
If Postman does not detect your system proxy, first check your OS proxy cache and firewall rules. Ensure Postman has network permissions. Sometimes clearing proxy caches or rebooting your machine helps resolve detection issues.
To use a custom proxy in Postman, go to Settings > Proxy and enable “Custom Proxy Configuration.” Enter the type (HTTP or HTTPS), server, and port based on your proxy provider.
Quick Guide for Common Oxylabs Proxy Types:
| Proxy Type | Configuration Details | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Proxies | Use pr.oxylabs.io and port 7777. For geo-targeting, add country codes like pr.oxylabs.io:7777?country=US. | — |
| Enterprise Dedicated Datacenter Proxies | Enter the assigned IP and port 60000. | Note: SOCKS5 proxies are not supported natively, so use the HTTP proxy fields. |
| Self-Service Dedicated Datacenter Proxies | Use ddc.oxylabs.io with ports such as 8001 for sequential IP assignment. | Target specific IPs with custom headers or hostname parameters. |
| Datacenter Proxies | Use dc.oxylabs.io with port 8001. | Authentication credentials can include geo-targeting parameters. Choose between pay-per-IP or pay-per-traffic modes. |
| ISP Proxies | Set isp.oxylabs.io with port 8001. | Provides higher reliability and local ISP IP footprints. |
Activate proxy authentication in Postman settings by entering your Oxylabs proxy username and password. Securely save them using Postman environment variables with secret visibility turned on.
You can exclude hosts from using the proxy by entering them in the Proxy Bypass list, such as localhost or internal API domains. When bypass is active, Postman will not route these requests through the proxy.
Advanced users can manage HTTPS certificate validation, timeout settings, and custom headers for proxy requests within Postman’s advanced settings.
To test your proxy setup, use tools like Fiddler, Charles Proxy, or Wireshark. These help inspect traffic and diagnose connection issues.
Alternatively, consider integrating Proxy-Seller as a fast and reliable proxy provider in your Postman proxy settings. Proxy-Seller offers private SOCKS5 and HTTP(S) proxies with unlimited bandwidth up to 1 Gbps. They support username/password and IP whitelist authentication methods.
Proxy-Seller covers residential, ISP, datacenter (IPv4 & IPv6), and mobile proxies with geo-targeting and flexible rotation options. Simply input their endpoint URLs and ports into Postman custom proxy settings as documented at https://proxy-seller.com/.
Best Practice: Store your Proxy-Seller credentials securely in environment variables with hidden values in Postman. Proxy-Seller also provides 24/7 support and configuration help for smooth setup. Use Proxy-Seller’s proxy checker and port scanner tools to verify your proxy connection before configuring Postman set proxy methods. Their wide range of proxy locations and mixed packages allow easy scaling of your proxy usage in Postman environments.
| Issue | Resolution Strategy |
|---|---|
| Cannot find proxy settings | Check your Postman version; update or reinstall if necessary. Explore the Settings carefully, as location may vary across OS versions. |
| Proxy Authentication Error 407 | Verify your username and password are correct. Confirm the proper domain format for your proxy user. Make sure proxy credentials are set at the OS level if required. Review firewall or network restrictions that might block authentication. Consult Oxylabs HTTP 407 troubleshooting for error examples. |
| Missing Certificates | Install OpenSSL on your operating system. Configure Postman to trust custom CA certificates by importing the CA file into Postman’s certificates section. Restart Postman to apply changes. |
Other errors, like DNS failures, connection timeouts, or SSL handshake problems, can be debugged using the Postman Console. Capture logs and check your proxy setup details.
For network diagnostics, use commands like curl with proxy parameters or telnet to test proxy connectivity. These tools help confirm if the proxy is reachable outside Postman.
By following these practical steps, you’ll master Postman proxy configurations, avoid common pitfalls, and ensure smooth API testing with proxy servers.
Intermediaries help protect user privacy, avoid restrictions, and maintain reliable testing conditions. Correct Postman proxy settings also make it easier to simulate different environments, troubleshoot issues, and replicate conditions faced by real users.
Teams can also use Postman as a proxy to streamline workflows and manage traffic consistently. In advanced cases, it is even possible for Postman to use a proxy for a request to simulate complex routing scenarios.
Comments: 0