
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski A browser fingerprint, or digital fingerprint, is a unique browser identifier that allows websites to track information about a user's browser and device. When a browser sends a request to a website, it exchanges data that makes up the digital fingerprint with the web server, allowing the target site to gather information about the user. This guide explains how to check browser Fingerprint and discusses different ways of changing it.
The fingerprint directly affects a user's anonymity online, as it includes information such as:
It is also worth mentioning Canvas Fingerprinting, a technology similar in function to the standard digital fingerprint but with some differences. This method uses the HTML5 Canvas element to create an invisible image in the user's browser, which is then converted into a unique digital code. Due to differences in how various browsers and devices render images, the code becomes unique to each user. This technology is often used in conjunction with standard fingerprinting to enhance the accuracy of user identification.
Browser Fingerprint works by collecting many different “signals” from your browser and device to create a unique profile. These signals include attributes like your browser type, screen resolution, installed fonts, and hardware details. By combining these diverse pieces of information, the systems build a high-entropy identifier. This identifier is unique enough to distinguish you even if your device is similar to others.
To keep this ID stable, fingerprinting tools weigh each signal by how unique and consistent it is over time. For example, your browser version changes less often than your IP address, so it holds more weight. Minor changes in your setup won't break the fingerprint; it adapts to maintain your persistent ID.
Scripts running in the background gather this data without slowing down or interrupting your experience. They collect info asynchronously, using fallbacks when certain browser APIs are not available.
A typical data collection flow looks like this:
There, statistical entropy calculations determine how unique your fingerprint is compared to others.
Advanced systems rely on machine learning and server-side analysis to improve reliability. They analyze patterns using algorithms like Random Forest or Neural Networks to increase identifier stability and detect anomalies.
Anti-fraud heuristics also apply. Systems detect suspicious behavior by clustering similar fingerprints, spotting outliers, and correlating user actions with their fingerprints. This helps prevent spoofing and enhances security.
Common frameworks and tools used include JavaScript fingerprinting libraries and machine learning models. These work together to collect, analyze, and verify signals in near real-time, making sure the fingerprint is accurate and hard to fake.
Initially, fingerprint technology was developed to prevent fraudulent activities online. For example, digital fingerprints were actively used by banking institutions to quickly and effectively identify suspicious activity on their sites. Over time, the functionality of this technology has expanded significantly, and it is now used in virtually all areas of Internet activity.
Many companies and web resources collect information about their visitors for further analysis of behavioral factors, such as what users pay attention to most often and which pages they visit the most. This information helps to later adjust the content on the resource and make personalized advertising more effective. For instance, if a user is surfing the internet on an outdated smartphone, various services, having this information, can offer personalized advertising for new-generation smartphones.
Another important role of fingerprinting is providing users with a website optimized for a specific device. Based on the digital fingerprint, the server understands from which device the site is being accessed and opens the appropriate version.
Thus, a fingerprint, along with the user's IP address, is their main identifier online, and to achieve the highest level of connection anonymization, it is necessary to change these parameters.
Using different digital fingerprints is beneficial, for example, when handling multiple accounts. By setting up separate fingerprints for different accounts, one can avoid unwanted blocks and associations between profiles, as the server will not be able to track that the accounts are being used by the same person. Next, we will look more closely at the options available to users for changing their digital fingerprint.
You’ll find that browser fingerprint test tools collect a wide range of attributes. These include basic details that create a basic profile:
But fingerprinting goes deeper with technical details, such as:
For example, font enumeration works by using JavaScript to measure text width when rendered in different fonts. This lets fingerprinting scripts identify which fonts you have installed – a unique device trait. Plugin detection no longer relies on the old plugin enumerations but now uses MIME type checks and feature detection.
To gather these data points, fingerprinting scripts tap into multiple browser APIs, including:
Popular demo tools like FingerprintJS, AmIUnique, and Panopticlick allow you to check browser fingerprint attributes and see their entropy, giving you a practical view of what’s being collected.
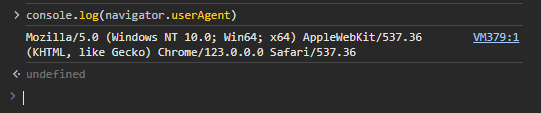
There are several ways to check your fingerprint, but not all of them are equally informative. Specific parameters of the digital fingerprint, such as the User-agent, can be determined using the browser's developer tools. To do this, press F12, navigate to the “Console” section, and enter the command – console.log(navigator.userAgent).
However, a more convenient way to check the digital fingerprint of a device is to use specialized online checkers such as:
To check your fingerprint just open the specialized website, and the information about the device will most often be displayed on the homepage. Let's provide examples of what this might look like.
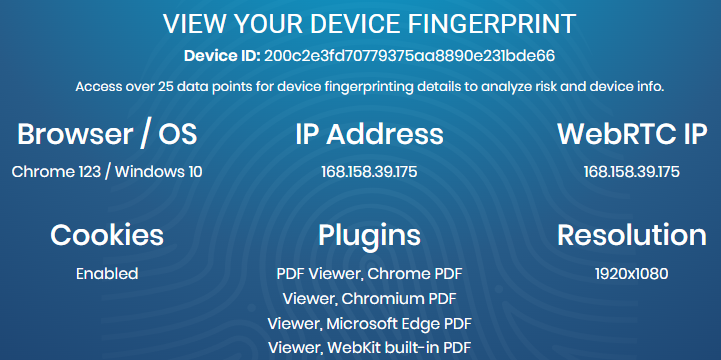
When changing the digital fingerprint later, online checkers can be used to verify whether the necessary parameters have changed and, if necessary, make further adjustments to the settings.
Changing the parameters of the digital fingerprint can significantly increase user anonymity online and also avoid blocks in the realm of multi-accounting. There are many ways to substitute a Fingerprint, each with its degree of effectiveness. Let's examine them in more detail:
Using just a proxy server, as well as working through anonymous mode in the browser, does not fully change the digital fingerprint, which makes their separate application ineffective. In turn, disabling plugins can affect the display of content on websites. Therefore, let's consider the two most effective methods: using specialized extensions and anti-detect browsers for changing the Fingerprint in conjunction with configuring a proxy server.
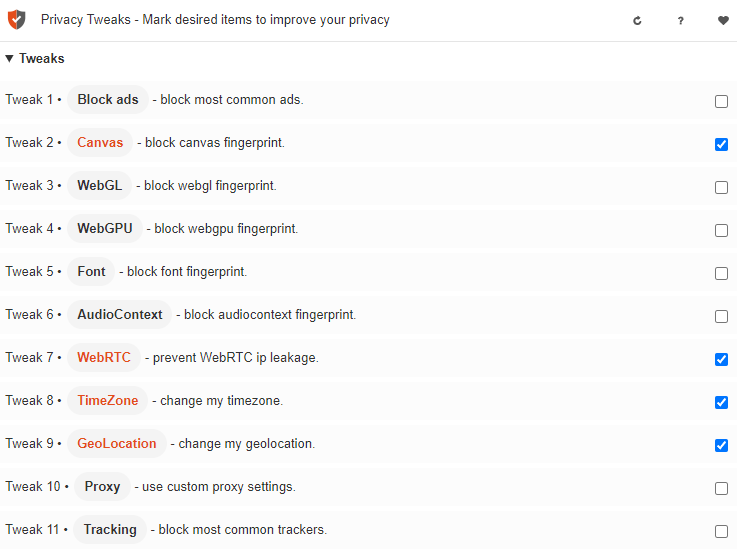
Plugins for managing digital fingerprints can be found in browser extension stores. These plugins allow blocking the transmission of certain fingerprint parameters to the target server to ensure a higher level of online anonymity. Let's see how this works using the “Privacy Tweaks” extension, available for Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.

On the main page of the extension in the “Tweaks” tab, there is a large number of switches that allow you to:
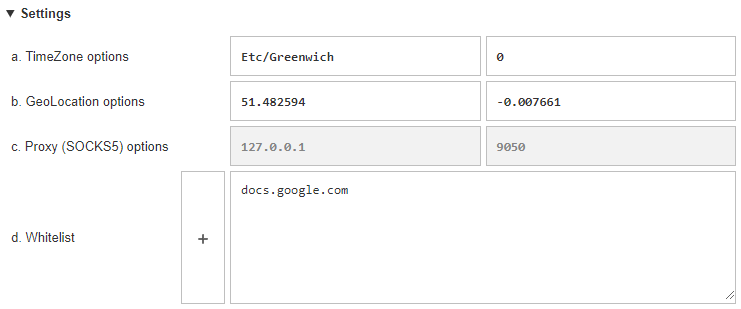
The “Settings” tab allows you to manually configure specific parameters, such as time zone, geolocation, proxy server, and the ability to add certain sites to the exceptions when working with the extension.
It is recommended to use Privacy Tweaks in conjunction with a private proxy server to provide an additional level of connection anonymization.
The most reliable method for substituting the Fingerprint is using anonymous browsers, many of which come with built-in functionality for precise configuration of these data. Let’s take a closer look at how to change digital fingerprint settings using the anti-detect browser AdsPower, which offers a free version with sufficient functionality for such purposes.

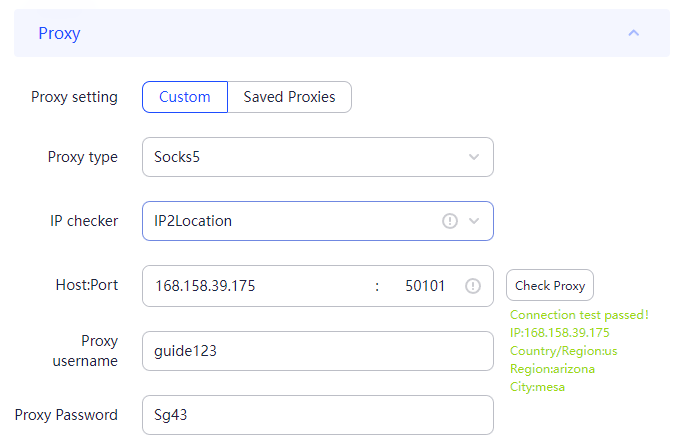
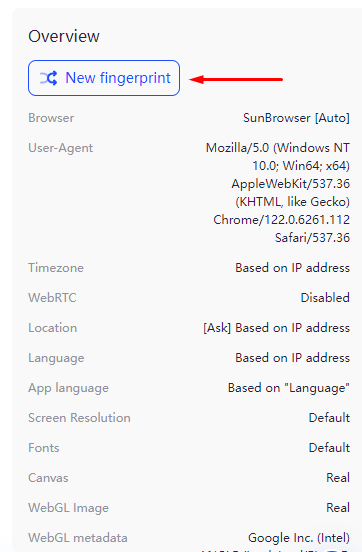
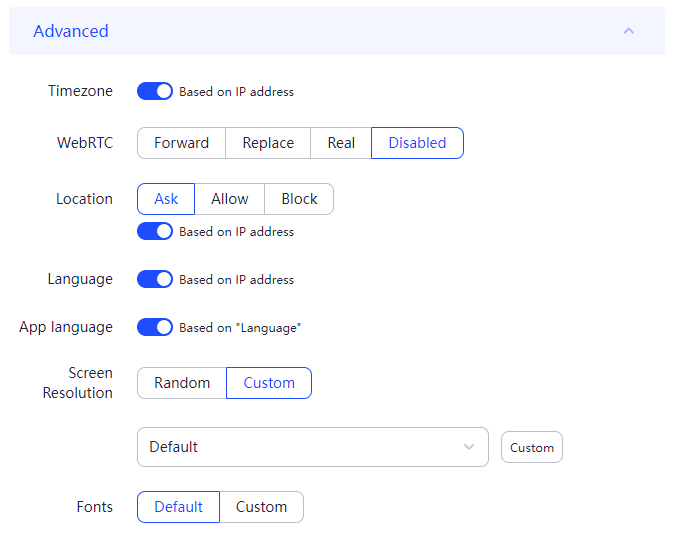
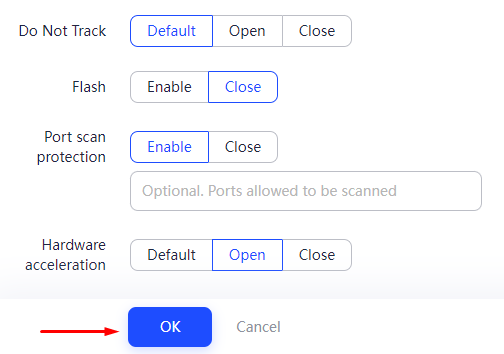
This completes the setup using the AdsPower browser. Most anti-detect browsers operate on a similar principle.
Understanding the major browser fingerprinting techniques helps you protect your privacy.
Additional techniques include:
Common JavaScript libraries, such as those within FingerprintJS, include modules for these techniques. However, modern browsers increasingly block or limit fingerprinting APIs.
To counter browser fingerprinting, you can use anti-fingerprint browsers designed to minimize exposed data and standardize fingerprints. But IP and geographic info can still reveal you.
Here, Proxy-Seller’s proxy services come in. By masking your IP address and location, Proxy-Seller reduces fingerprint uniqueness tied to your network. It offers fast, private SOCKS5 and HTTPS proxies with geo-targeting, covering residential, ISP, datacenter, IPv4, IPv6, and mobile proxies. Their high bandwidth and flexible API integrate smoothly with scraping or data collection tools, helping you evade fingerprinting that depends on IP and location signals.
Using Proxy-Seller alongside anti-fingerprint browsing techniques strengthens your anonymity and makes it harder for trackers to reliably identify you. Keeping an eye on your browser fingerprint test results regularly will help you maintain better privacy against these evolving tracking methods.
It should be noted that the best solution would be to use anti-detect browsers in combination with proxies, which allows for a complete alteration of the fingerprint. This option is suitable for work in the fields of website promotion, cryptocurrencies, and advertising. For simpler tasks, users can use special browser extensions.
Comments: 0