
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski Companies are seeing stricter requirements for data protection, process automation, and the reliability of online services. In this context, the reason why you need to use a proxy server is clear: they help control network traffic, balance workloads across teams, and provide secure access to corporate systems. Below are ten core reasons why intermediating servers have become an integral part of IT and marketing infrastructure.
IT teams need visibility into network traffic and controls that prevent leaks. Proxies provide a secure gateway for developers connecting to internal services and test environments. Traffic is encrypted and the real IP address is masked. This is especially useful in CI/CD pipelines, where hundreds of automated requests are sent every day.
Corporate intermediary servers distribute load among departments and regulate network activity. You can set distinct access policies for HR, Finance, and IT, reducing the risk of user error and ensuring transparent oversight. For major banks and telecoms, this approach became standard in 2026.
For analytics and e-commerce, proxies underpin large-scale web scraping. Automated systems collect millions of data rows daily–from competitor pricing to stock availability. With such intermediaries, these workflows run smoothly and within platform limits, which is critical in online retail where speed directly affects revenue.
Teams that operate multiple ad accounts must keep session access stable. Proxies let you allocate and rotate IP addresses for session management, making agency operations more predictable and resilient. Organizations in this space are advised to use a proxy server to minimize campaign disruptions across markets.
SEO and marketing teams rely on new IPs to automate tasks that don’t scale by hand: monitoring rankings across thousands of queries, collecting snippets, checking indexation, and testing SERP changes.
Proxies distribute requests across hundreds of IPs, avoiding overload and temporary rate limits from search engines. In digital agencies, these pipelines are part of reporting: scripts collect data daily and build client reports.
They’re also used for local growth initiatives, enabling analysis of search results in different countries or cities and adapting SEO strategies to specific markets–especially relevant for international companies operating in several language segments.
Each protocol addresses a specific need, for example:
| Protocol | Used For | Business Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | API, web requests | High speed |
| HTTPS | Financial services, web surfing, SaaS — the traditional cloud computing model providing software | Encryption |
| SOCKS | Analytics, automation | Versatility, encryption |
Organizations with distributed offices need protected access. Intermediaries let IT centralize connection management and control employee traffic across countries.
They also help segment network permissions by role: developers get full access to test environments, while managers are limited to CRM and corporate email.
In hybrid environments, they integrate with monitoring and logging systems to track activity and respond quickly to potential threats.
In markets for limited releases–sneakers, collectibles, gadgets–resellers use automated purchasing systems. Proxies distribute IP addresses to keep connections stable and operate within application limits during high-volume demand.
For companies in this niche, they are a competitive edge: acting faster and scaling procurement across regions simultaneously. Corporate servers also support local price and trend analysis, enabling data-driven resale strategies with fewer human errors.
Caching and request optimization reduce server load and speed up data access. For SaaS platforms, that means more predictable resource allocation; for media holdings, it’s the ability to serve millions of users without delays.
Proxies can also lower infrastructure costs: frequently accessed resources are served faster, and internal systems experience fewer interruptions. In large enterprises, this cuts cloud spend and lets IT reallocate capacity to higher-priority work.
Such intermediaries are becoming part of strategic infrastructure–used for data protection, process automation, and working with large datasets. That’s a key reason to adopt them now and for the long term. In the coming years, proxy-based solutions will be especially active in fintech, e-commerce, SaaS, and media: financial institutions will add layers of protection for client transactions; online retailers will run global market monitoring; and SaaS companies will maintain stable interactions with customers worldwide. The role of proxies in B2B will continue to grow.
According to why our clients purchase them, we can identify the most common business use cases.
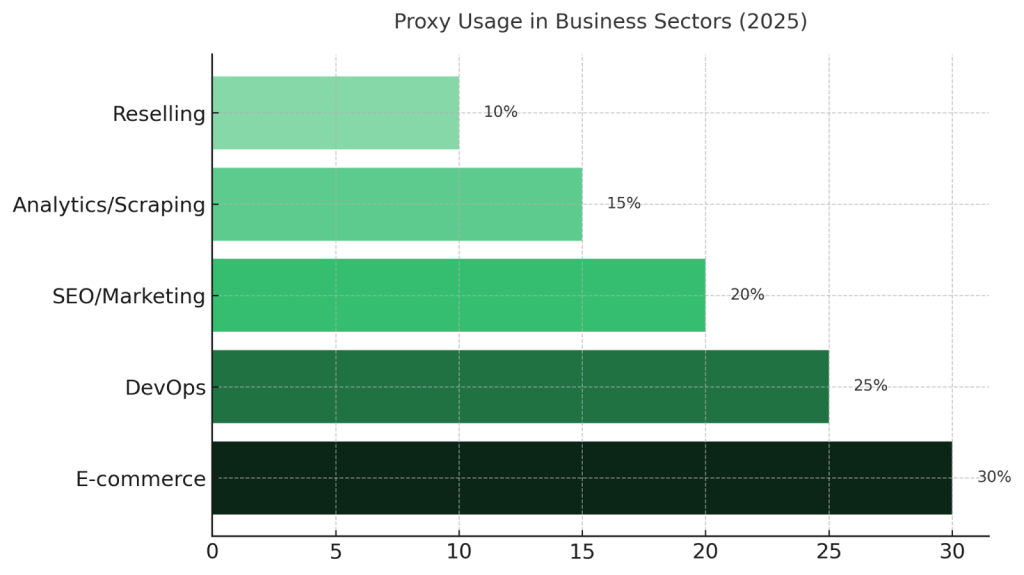
They help IT teams secure infrastructure, marketers scale campaigns, analysts collect large data volumes, and resellers stay competitive in limited-release markets. For businesses, this is a compelling reason to treat proxy servers as a component of corporate strategy rather than a set of isolated tools.
To make integration as productive as possible, consider specialized tooling. For example, our “Top 8 Proxy Plugins” roundup can speed up implementation in day-to-day workflows and improve overall network efficiency.
It protects data, supports scalability, and automates essential processes.
It enables confidential access and centralized connection management.
They provide fast handling of APIs and web requests.
SOCKS are versatile and suitable for scraping, SEO tasks, and multi-service projects.
They improve the security of remote staff and sensitive information, help manage traffic, and scale network processes.
Comments: 0