
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski Web scraping Airbnb Python and scraping Airbnb data is crucial for analyzing the real estate market, researching rental price dynamics, conducting competitive analysis, and assessing reviews and ratings. This can be accomplished by scraping techniques. However, accessing this information can be challenging, as scraping may violate the terms of use of the site.
Next, we will explore a step-by-step guide on how to develop a web scraper using Python and Selenium to scrape Airbnb listings. This guide will also cover how to avoid potential blocks and restrictions imposed by the platform.
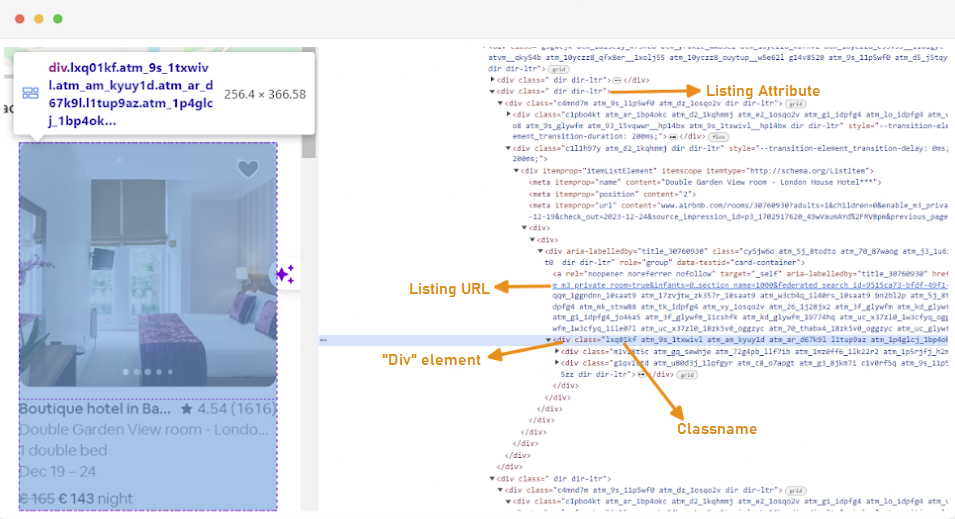
The first step in creating a web scraper is understanding how to access the web pages you're interested in, since the structure of websites can often change. To familiarize yourself with the structure of a site, you can use the browser's developer tools to inspect the HTML of the web page.
To access Developer Tools, right-click on the webpage and select “Inspect” or use the shortcut:
Each listing container is wrapped in a div element with the following attribute: class="g1qv1ctd”.
By clicking on "location" and typing "London, UK" we can access the location offered in London. The website suggests adding check-in and check-out dates. It allows them to calculate the price of the rooms.
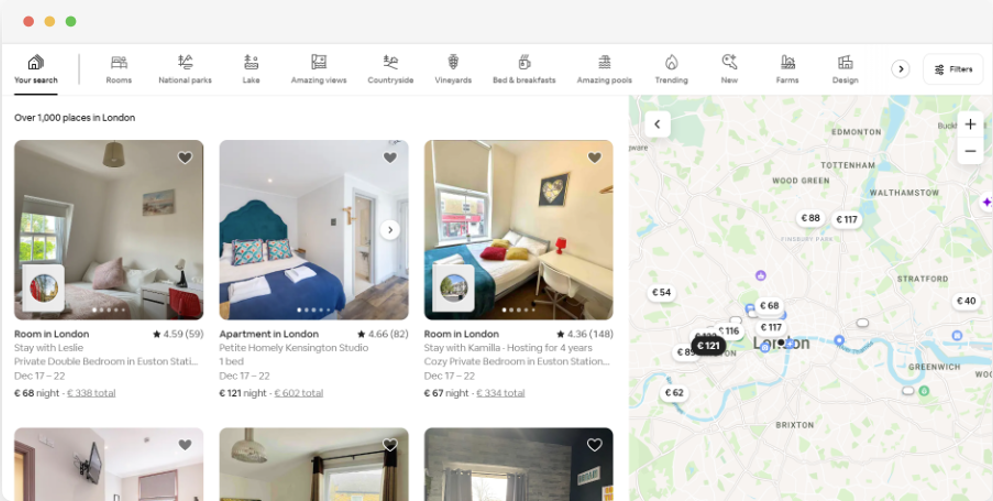
The URL for this page would look something like this:
url = "https://www.airbnb.com/s/London--United-Kingdom/homes?tab_id=home_tab&refinement_paths%5B%5D=%2Fhomes&flexible_trip_lengths%5B%5D=one_week&monthly_start_date=2024-01-01&monthly_length=3&price_filter_input_type=0&channel=EXPLORE&query=London%2C%20United%20Kingdom&place_id=ChIJdd4hrwug2EcRmSrV3Vo6llI&date_picker_type=calendar&source=structured_search_input_header&search_type=autocomplete_click"From the search page, we will scrape the following attributes of the product listing data from Airbnb:
You’ll learn how to use powerful tools to scrape Airbnb data efficiently. Start with the Apify platform, designed specifically for scraping and crawling tasks.
The Apify platform has multiple components useful for scraping Airbnb listings:
If you want to build your own Airbnb data scraping solution with Python, consider these popular libraries and tools:
| Tool/Library | Primary Function | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Requests + BeautifulSoup | Fetch HTML and parse static content. | Simple, static data extraction where JavaScript is not involved. |
| Selenium WebDriver | Interact with dynamic content and pages requiring user interaction (clicking, scrolling). | Dynamic content and user interaction simulation. |
| Playwright Python | Faster and more reliable headless browser automation. | Scraping Airbnb data behind login or dynamically changing content. |
| Scrapy Framework | Advanced and scalable scraping framework with built-in pipelines. | Large-scale Airbnb data scraping projects. |
Proxies are critical for scraping Airbnb without getting banned or stuck on CAPTCHAs. Without proxies, your IP address will quickly get blocked.
Types of proxies include:
Popular proxy sellers include ProxySeller, Bright Data, Oxylabs, and Smartproxy.
Proxy-Seller stands out as a reliable, versatile supplier offering IPv4, IPv6, ISP, residential, and mobile proxies. They cover over 220 countries and provide high-speed connections up to 1 Gbps, 99% uptime, and 24/7 customer support.
Proxy-Seller offers various proxy rotation methods like sticky sessions and time/request-based rotation, helping you manage IP bans and keep your scraping runs smooth and efficient. Their easy dashboard, API for proxy management, and flexible rental periods with bulk discounts make them excellent for both individuals and enterprises scraping Airbnb data.
To start web scraping Airbnb Python data, you need to set up your development environment first. Here are the steps to do that:
Virtual environments allow you to isolate Python packages and their dependencies for different projects. Every project’s dependencies are guaranteed to be accurate when no cross-project interference exists.
Windows users can create a virtual environment titled “venv” by opening a command prompt with administrator privileges and running the command:
python -m venv venvTo activate the newly created virtual environment, run the command:
venv\Scripts\activateOpen a terminal and execute the command below to set up a new virtual environment dubbed “venv”:
sudo python3 -m venv venvActivate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activateTo deactivate the virtual environment, simply run the following command:
deactivateNow that you have a virtual environment set up, you can install the necessary libraries.
Within your activated virtual environment, run the following command to install the required libraries:
pip install selenium beautifulsoup4 lxml seleniumwireSelenium requires a driver to interface with the chosen browser. We will use Chrome for this guide. However, please ensure you have installed the appropriate WebDriver for the browser of your choice.
Once downloaded, ensure the driver is placed in a directory accessible by your system's PATH environment variable. This will allow Selenium to find the driver and control the browser.
As mentioned above, the first thing to do is to import the Selenium Wire and BeautifulSoup libraries into your Python file. This is how it looks:
from seleniumwire import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
import csv
import randomWe will also import the `random`, `time`, and `csv` libraries for various utilities.
Next, we define a list of proxies to avoid being blocked by Airbnb. When trying to send a request without a premium proxy, you may encounter an "Access Denied" response.
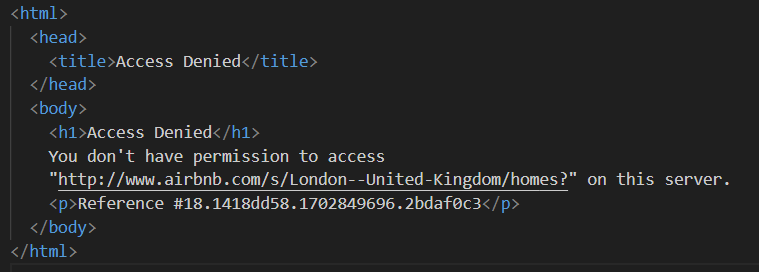
You can set up a proxy as follows:
# List of proxies
proxies = [
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port1",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port2",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port3",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port4",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port5",
]Make sure you customize the “YourproxyIPAddress” and ”Yourproxy_port” fields with the corresponding information modulus your proxy address from Proxy-seller. Also do not forget to change the placeholders “username” and “password” with your actual credentials.
Rotating proxies is a vital step in web scraping. Websites often block or restrict access to bots and scrapers when they receive multiple requests from the same IP address. By rotating through different proxy IP addresses, you can avoid detection, appear as multiple organic users, and bypass most anti-scraping measures implemented on the website.
To set up rotation, import the “random” library. We also define a function `get_proxy()` to select a proxy from our list. This function randomly selects an item from the list of proxies using the random.choice() method.
def get_proxy():
return random.choice(proxies)Next, we define the main function called `listings()`. This is where we’ll set up our “ChromeDriver”. This function uses Selenium to navigate the property listings page, waits for the page to load, and parses the HTML using Beautiful Soup.
def listings(url):
proxy = get_proxy()
proxy_options = {
"proxy": {
"http": f"http://{proxy}",
"https": f"http://{proxy}",
"no_proxy": "localhost,127.0.0.1",
}
}
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument("--headless")
s = Service(
"C:/Path_To_Your_WebDriver"
) # Replace with your path to ChromeDriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome(
service=s, seleniumwire_options=proxy_options, chrome_options=chrome_options
)
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(8) # Adjust based on website's load time
soup = BeautifulSoup(driver.page_source, "lxml")
driver.quit()To scrape Airbnb using Python, we start by selecting a random proxy and setting up the options. These options will be used to configure the webdriver. Next, we set up the Chrome options. Add the --headless argument to run the browser in headless mode, which means that the browser will run in the background without a graphical user interface.
Then initialize the webdriver with the service, Selenium Wire options, and Chrome options. The webdriver is then used to navigate to the given URL. We add a sleep time of 8 seconds to allow the page to load completely and then parse the returned HTML using Beautiful Soup. After the parsing is done, it closes the webdriver.
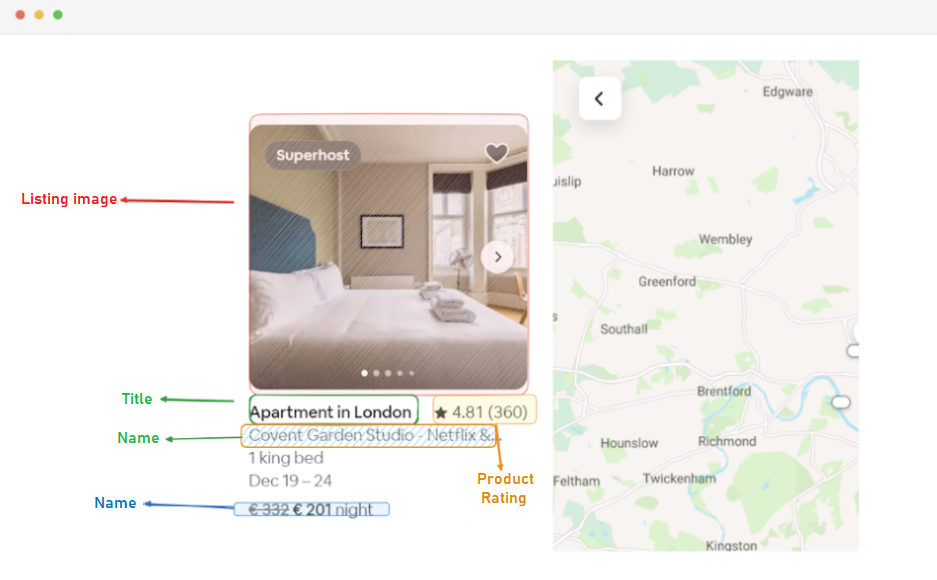
Once you have successfully obtained the HTML content, the next step is to extract relevant data for each property. Using BeautifulSoup, we can easily navigate through the structure and locate the sections containing the necessary information.
First, we identify all the blocks on the page that hold property details. These sections include the URL, title, description, rating, price, and any additional info.
listing_elements = soup.find_all("div", class_="g1qv1ctd")
for listing_element in listing_elements:This code uses BeautifulSoup's find_all() method to locate all div tags with the class “g1qv1ctd”. Each of these represents a single property on the Airbnb page. It then loops through them to gather the relevant data.
URL_element = soup.find("a", class_="rfexzly")
listing_data["Listing URL"] = (
"https://www.airbnb.com" + URL_element["href"] if URL_element else ""
)We search within our soup object for an anchor tag with the class “rfexzly”. If found, it extracts the 'href' attribute (which contains the relative URL) and combines it with the base URL to create the full address. If not found, an empty string is used to avoid errors.
Next, we grab the title, which is inside a div tag with the class “t1jojoys”. We retrieve and clean the text. If the tag isn’t present, we simply store an empty string.
title_element = listing_element.find("div", class_="t1jojoys")
listing_data["Title"] = (
title_element.get_text(strip=True) if title_element else ""
)Description_element = listing_element.find("span", class_="t6mzqp7")
listing_data["Description"] = (
Description_element.get_text(strip=True) if Description_element else ""
)Similar to how we get the title, this part finds a span tag with the class "t6mzqp7". We extract and clean the text content, which holds a short description of the property.
rating_element = listing_element.find("span", class_="ru0q88m")
listing_data["Rating"] = (
rating_element.get_text(strip=True) if rating_element else ""
)As shown in the code above, a span tag with the class “ru0q88m” holds the rating value. We extract and clean it to remove extra spaces.
Finally, we extract the price.
price_element = listing_element.select_one("._1y74zjx")
listing_data["Price"] = (
f"{price_element.get_text(strip=True)} per night" if price_element else ""
)This code locates the element with the class "_1y74zjx" within the current listing_element. If this element, which typically contains the price information, is found, its text content is extracted, cleaned, and appended with "per night" to form a more informative price string.
Some properties may include extra details.
listing_info_element = listing_element.find("span", {"aria-hidden": "true"})
listing_data["Additional Listing information"] = (
listing_info_element.get_text(strip=True) if listing_info_element else ""
)We search for a span tag with the attribute aria-hidden="true" to locate this extra information. After gathering all the relevant data from a single property, we add it to our list:
listings.append(listing_data)Once all listings have been processed, we return the list of listings, each represented as a dictionary containing the extracted data.
return listings
After successfully scraping data from Airbnb's pages, the next important step is storing this valuable information for future analysis and reference. We use the csv library for this task. We open a CSV file in write mode and create a csv.DictWriter object. We then write the header and the data to the file.
airbnb_listings = listings(url)
csv_file_path = "proxy_web_listings_output.csv"
with open(csv_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8", newline="") as csv_file:
fieldnames = [
"Listing URL",
"Title",
"Description",
"Rating",
"Price",
"Additional Listing information",
]
writer = csv.DictWriter(csv_file, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
for listing in airbnb_listings:
writer.writerow(listing)
print(f"Data has been exported to {csv_file_path}")Here is the complete Python code to scrape Airbnb we used for this tutorial:
from seleniumwire import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
import csv
import random
# List of proxies
proxies = [
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port1",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port2",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port3",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port4",
"username:password@Your_proxy_IP_Address:Your_proxy_port5",
]
def get_proxy():
return random.choice(proxies)
def listings(url):
proxy = get_proxy()
proxy_options = {
"proxy": {
"http": f"http://{proxy}",
"https": f"http://{proxy}",
"no_proxy": "localhost,127.0.0.1",
}
}
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument("--headless")
s = Service(
"C:/Path_To_Your_WebDriver"
) # Replace with your path to ChromeDriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome(
service=s, seleniumwire_options=proxy_options, chrome_options=chrome_options
)
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(8) # Adjust based on website's load time
soup = BeautifulSoup(driver.page_source, "lxml")
driver.quit()
listings = []
# Find all the listing elements on the page
listing_elements = soup.find_all("div", class_="g1qv1ctd")
for listing_element in listing_elements:
# Extract data from each listing element
listing_data = {}
# Listing URL
URL_element = soup.find("a", class_="rfexzly")
listing_data["Listing URL"] = (
"https://www.airbnb.com" + URL_element["href"] if URL_element else ""
)
# Title
title_element = listing_element.find("div", class_="t1jojoys")
listing_data["Title"] = (
title_element.get_text(strip=True) if title_element else ""
)
# Description
Description_element = listing_element.find("span", class_="t6mzqp7")
listing_data["Description"] = (
Description_element.get_text(strip=True) if Description_element else ""
)
# Rating
rating_element = listing_element.find("span", class_="ru0q88m")
listing_data["Rating"] = (
rating_element.get_text(strip=True) if rating_element else ""
)
# Price
price_element = listing_element.select_one("._1y74zjx")
listing_data["Price"] = (
f"{price_element.get_text(strip=True)} per night" if price_element else ""
)
# Additional listing info
listing_info_element = listing_element.find("span", {"aria-hidden": "true"})
listing_data["Additional Listing information"] = (
listing_info_element.get_text(strip=True) if listing_info_element else ""
)
# Append the listing data to the list
listings.append(listing_data)
return listings
url = "https://www.airbnb.com/s/London--United-Kingdom/homes?tab_id=home_tab&refinement_paths%5B%5D=%2Fhomes&flexible_trip_lengths%5B%5D=one_week&monthly_start_date=2024-01-01&monthly_length=3&price_filter_input_type=0&channel=EXPLORE&query=London%2C%20United%20Kingdom&place_id=ChIJdd4hrwug2EcRmSrV3Vo6llI&date_picker_type=calendar&source=structured_search_input_header&search_type=autocomplete_click"
airbnb_listings = listings(url)
csv_file_path = "proxy_web_listings_output.csv"
with open(csv_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8", newline="") as csv_file:
fieldnames = [
"Listing URL",
"Title",
"Description",
"Rating",
"Price",
"Additional Listing information",
]
writer = csv.DictWriter(csv_file, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
for listing in airbnb_listings:
writer.writerow(listing)
print(f"Data has been exported to {csv_file_path}")The code segment guarantees that any data collected by the scraper is kept in a file called "proxyweblistings_output.csv" in CSV format.
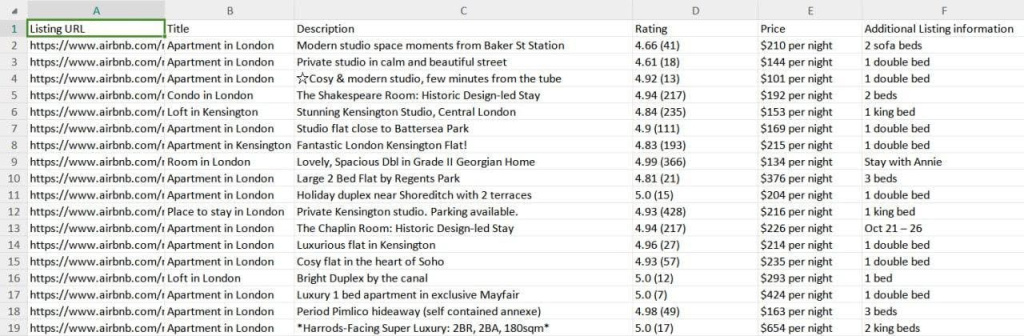
The results of our scraper are saved to a CSV file called “proxy_web_listings_output.csv”, as seen below.
You’ll learn how to scrape Airbnb listings data without writing code by using the Apify Airbnb Scraper.
Visit the Apify Store and locate the Airbnb Scraper product page. You can easily create an account with Google, GitHub, or email sign-up. The free trial lets you try the scraper with limited usage, so you can test it before committing.
Choose areas or listings carefully to balance between data volume and relevance.
Customize your scraper with these options:
Use toggles or JSON parameters to set these options. Test configurations with small runs before ramping up to large data sets.
Launch your scraping task via the Apify web interface or API call. Monitor progress using built-in indicators, review error logs, and take advantage of automatic retries. Estimated runtimes depend on query size and concurrency settings. Avoid bans by managing concurrency and respecting rate limits.
Once the scraping is complete, export the data from the Output and Storage tabs. Formats include JSON, CSV, Excel XLSX, HTML, XML, and RSS. Each suits different use cases:
Preview large datasets with filters or spreadsheet software. Post-process data with Pandas (Python), Excel Power Query, or SQL databases. Use the data in analytics dashboards like Power BI or Tableau for insights.
Scraping Airbnb data brings challenges. Expect issues like IP blocking, CAPTCHAs, dynamic content loading, AJAX pagination, and anti-bot detection. Here’s how to solve them:
| Obstacle | Solution Strategy |
|---|---|
| IP blocking and Rate Limiting | Use proxy rotation (Proxy-Seller) to switch IPs and reduce detection risk. Throttle requests and add randomized delays. |
| Dynamic Content/AJAX Pagination | Automate browsers with headless tools like Playwright or Puppeteer for dynamic pages. |
| CAPTCHAs | Integrate CAPTCHA solving services (2Captcha, Anti-CAPTCHA) to bypass CAPTCHAs automatically. |
| Bot Detection | Spoof request headers (e.g., user-agent strings) to mimic real browsers. Rotate user-agents. |
| Behavioral Analysis | Add randomized delays and movement patterns to imitate human browsing patterns. |
Regularly monitor scraper logs and error reports. Adapt the parameters dynamically if you notice blocks or slowdowns.
If scraping fails, consider these fallback methods:
By anticipating these obstacles and using these techniques, you’ll maintain consistent Airbnb data scraping results and maximize data accuracy.
This guide effectively explains how to scrape Airbnb data listings using Python, enabling the extraction of key details such as prices, availability, and reviews. It emphasizes the importance of using proxies and rotating them to prevent being blocked by Airbnb's anti-bot measures.
Scraping Airbnb data Python and Selenium give you direct access to valuable information like pricing and availability – key insights for market research, investment analysis, or even building your own real estate tools. While the process comes with technical challenges (and some legal gray areas), setting up the right environment, understanding how the website works, and using tools like proxies and headless browsers can help you get around most obstacles. Just be sure to respect the platform’s terms of use and always handle the data responsibly.
Comments: 0