
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski In the context of business automation, stable access to internet resources and the avoidance of blocks are crucial for effective interaction online. Technologies such as IP rotation and proxy pools play key roles in this area. These strategies not only optimize data collection, monitoring, and automation processes but also substantially minimize the risks associated with access restrictions to web resources.
The remainder of the article will explore the differences between IP rotation and proxy pools, detailing how each contributes to enhancing the efficiency of automated tasks.
IP rotation and proxy pools are closely related concepts, often utilized together to enhance web scraping and data mining effectiveness. Let’s examine each one in detail to understand their distinct roles and differences.
IP rotation is a technique where IP addresses are automatically changed either with each request or at predefined intervals. This approach is particularly effective for activities involving high-volume data collection or extensive querying of a single resource. The main objective of IP rotation is to prevent blocking by spreading the requests across various IP addresses, thereby simulating multiple users. This technique not only helps in maintaining anonymity but also ensures consistent access to resources that have protections against automated access.
Types of proxies that utilize IP rotation include:
Proxy servers that support IP rotation are often referred to as dynamic proxies. In this setup, the user is assigned a gateway server or “mask” IP address, behind which multiple IP addresses are available for use. It's important to note that while users can select a country and, for mobile proxies, a telecom operator, they do not see the specific IP addresses that will be used. Special IP checkers can be used to verify the current IP address.
Dynamic IP rotation can be configured in various ways, with the most common methods being rotation by time and rotation by link. Time-based rotation changes the IP address at set intervals, such as every 5 minutes, while link-based rotation changes the IP with each new request to the server. The choice of rotation model is typically made at the time of proxy purchase, tailored to fit the specifics of the user's tasks and automation needs.
A proxy pool consists of a pre-assembled collection of proxy servers with various IP addresses, typically established by the user. To create a proxy pool, users generally purchase the desired number of IP addresses, with each IP potentially located in a different geographic region. Static proxies are commonly employed to build these pools, including:
By setting up a pool of static proxies, users can deploy them across various scenarios. For example, if performing automation tasks, the user can integrate the pool into a script and program IP rotation. Alternatively, special tools such as browser extensions can manage IP changes based on user-defined rules, offering flexibility in how the proxies are utilized.
It's essential to recognize that the concept of a proxy pool applies to both residential and mobile proxies. Within this framework, the IP address of the gateway server grants access to a pool of IP addresses, among which dynamic proxies rotate. For instance, with mobile proxies, a pool might consist of IP addresses provided by a specific mobile operator in a chosen country. In the case of residential proxies, a pool includes IP addresses from real users' devices that are online and distributing traffic within a selected location.
Thus, the concepts of IP address rotation and proxy pools are closely intertwined. The main distinction lies in their definitions: a proxy pool refers to a set or list of IP addresses, while rotation refers to the process of changing these addresses.
Additionally, understanding the differences between dynamic and static proxies is crucial, as the relevance of rotation and proxy pools varies between them. For more detailed insights into how these concepts differ, consider exploring our article on the differences between static and dynamic proxies.
IP rotation and proxy pools play a crucial role in various business automation processes, demonstrating their utility across different domains:
Additionally, proxy rotation seamlessly integrates with various business applications, allowing users to incorporate it into their web scraping solutions regardless of the coding language used.
These applications underscore the advantages of using IP rotation and proxy pools, including scalability, anonymity, and uninterrupted access to critical data, thereby empowering businesses to conduct thorough competitive analyses, manage social media effectively, and carry out extensive SEO research without performance setbacks, even with substantial data volumes.
When selecting a proxy server for automating business processes, several critical factors must be taken into account:
Considering these factors is essential for ensuring the smooth operation of web resources and the effective implementation of automated business processes. Our customers can find our solutions suitable for most use cases, and the cost of services may significantly decrease thanks to our partners' proxy discounts.
There are numerous methods available for setting up and utilizing IP rotation and integrating proxy pools to automate tasks. Among these, anti-detect browsers stand out as particularly convenient and effective for managing these processes. Anti-detect browsers simplify the downloading and management of multiple proxy servers, thereby maintaining anonymity and preventing the linkage of accounts or profiles. An example of such a tool is AdsPower, known for its user-friendly interface and robust features for proxy integration and automation across various profiles. Here's how to integrate proxies with rotation and pools using AdsPower, starting with the setup of a single proxy that supports automatic IP changes, which can be either residential or mobile:
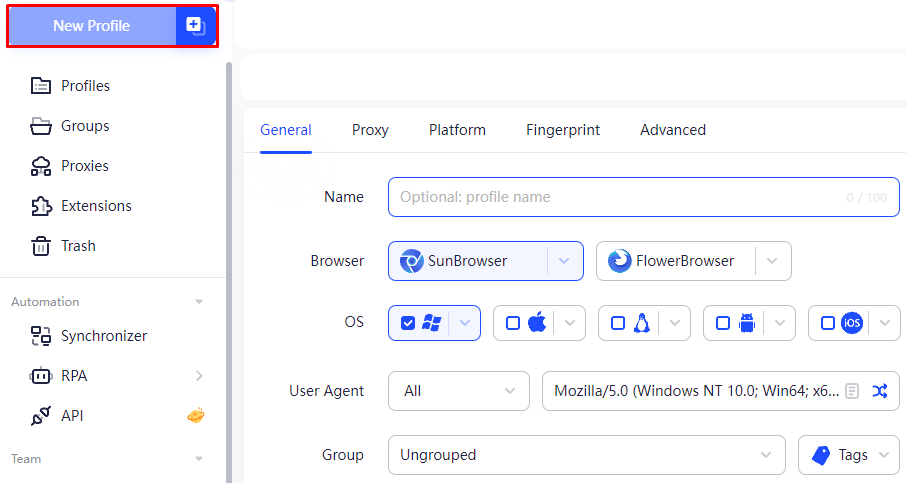
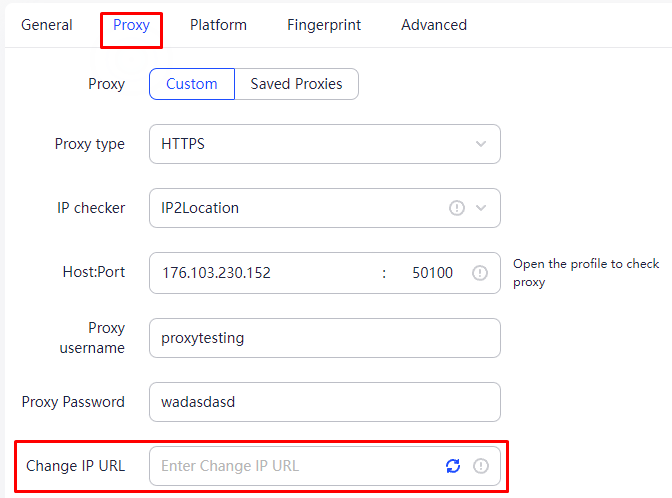
Here’s how to set up a pool of static proxy servers:
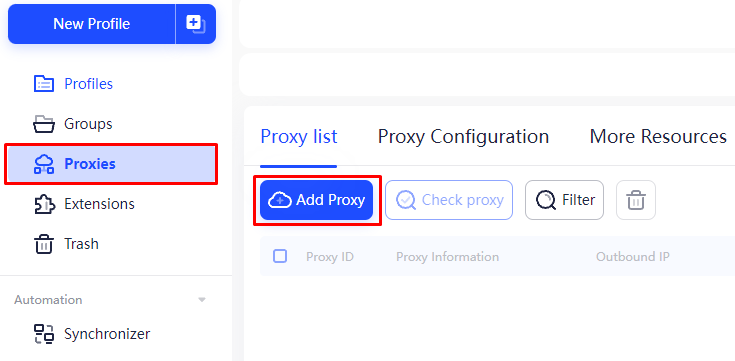
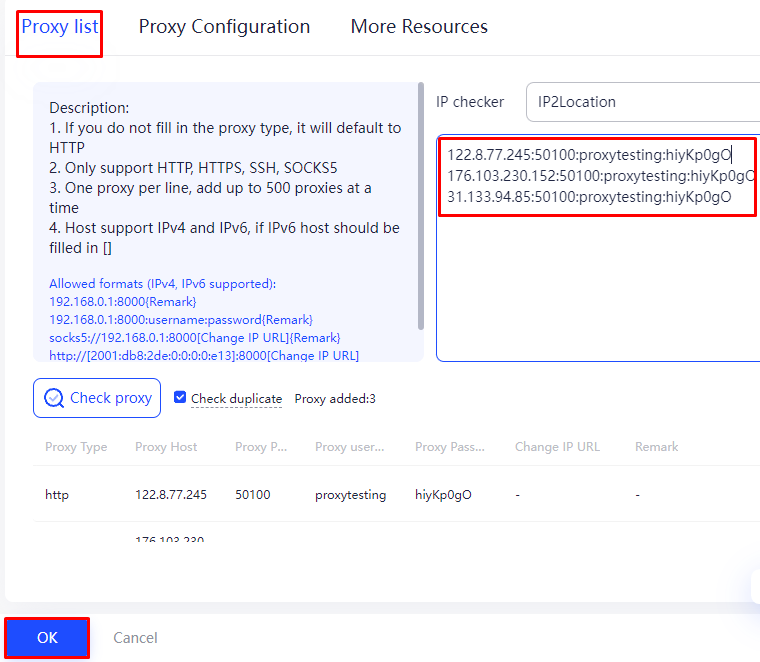
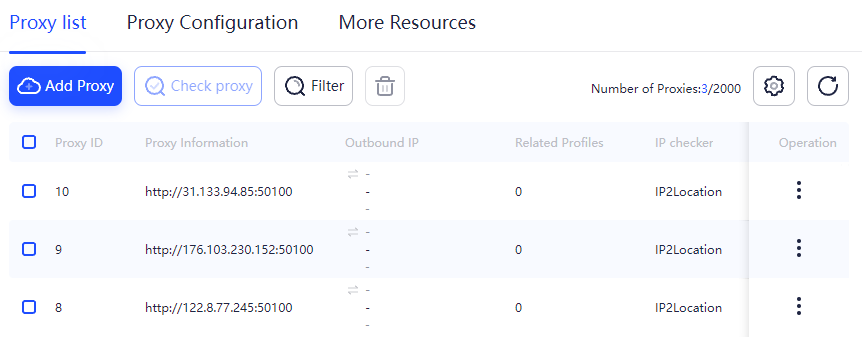
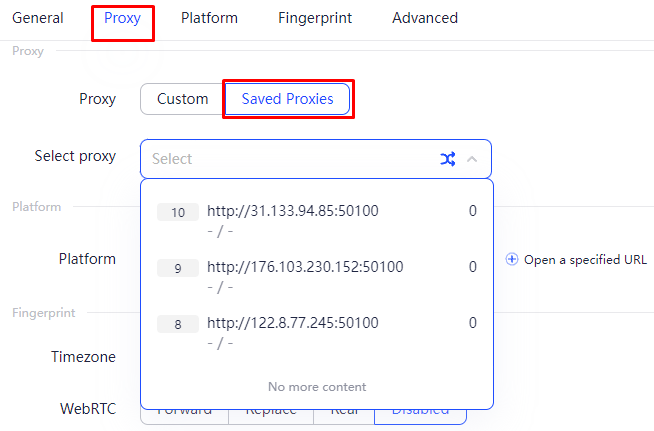
This proxy setup in AdsPower facilitates the automation of business processes related to managing multiple accounts and online activities. The ability to swiftly change the IP address with a single click and seamlessly integrate a proxy pool enhances flexibility and stability when interacting with web resources.
Using AdsPower as an example, we demonstrated a practical approach to configuring both individual proxies with automatic rotation and comprehensive proxy pools for managing multiple profiles. However, beyond AdsPower, various other tools and methods are available to efficiently handle IP rotation and proxy pools. These include specialized APIs, web scraping frameworks, and programs designed for managing Internet traffic. Selecting the most suitable solution depends on the specific business tasks at hand and the extent of automation required.
Comments: 0