
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski Disabling JavaScript is a step towards a simple and clean internet. Having done it, you will notice that the page loading speed will increase. Also, a huge number of distractions will disappear on sites: advertising, features with infinite scrolling of pages, and pop-ups. To get into this minimalistic world, you just need to figure out how to disable JavaScript in popular browsers.
Below we will attach the instructions for Chrome, Opera, Firefox, Safari, and Explorer/Edge.
You’ll learn how to disable JavaScript across the most popular browsers, both on desktop and mobile. This will help you control scripts for privacy, faster browsing, or troubleshooting.
To disable JavaScript in Opera, follow our instructions:
On the Mozilla browser, the process looks a little different, but in general it is also uncomplicated, even for novice computer users. To turn off JavaScript, follow the instructions below:
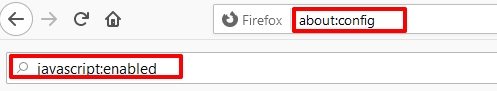

On Firefox for Android, the process is the same using about:config and toggling javascript.enabled.
That`s all, disabling JavaScript on Firefox is completed.
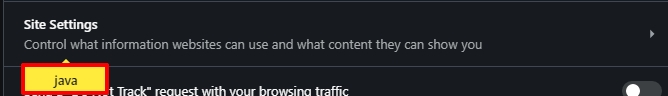
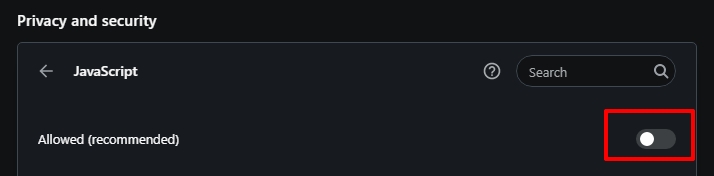
In this browser, the option is deactivated through the settings. To disable JavaScript in Google Chrome, you need to take 5 simple steps:
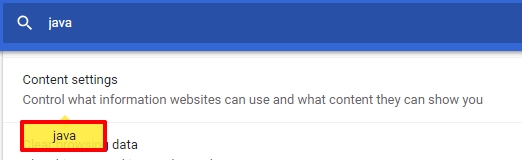
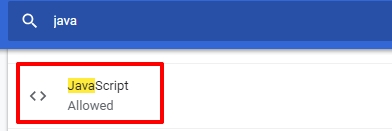

On Chrome Android, open Chrome > Settings > Site Settings > JavaScript, then toggle it off.
Disabling JavaScript in Google Chrome was completed successfully. Read also a useful article about the best proxy extensions for Google Chrome.
To deactivate JavaScript in Safari, follow the instructions:
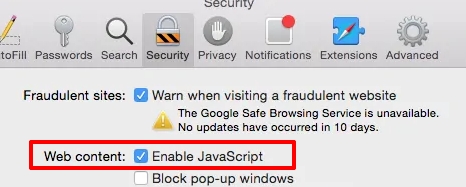
On iOS devices, open Settings > Safari > Advanced. - Toggle off JavaScript.
Note that iOS has system-level restrictions, so disabling JavaScript on mobile Safari may not block all scripts as completely as on macOS.
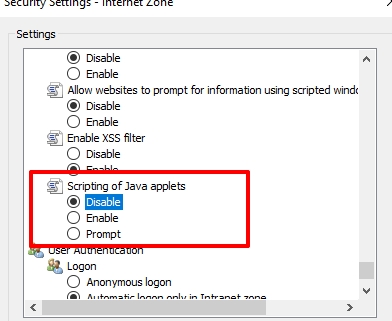
To deactivate JavaScript in Internet Explorer, you need to follow a simple instruction:
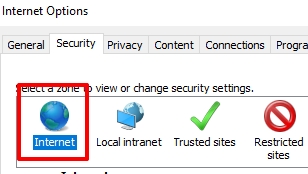
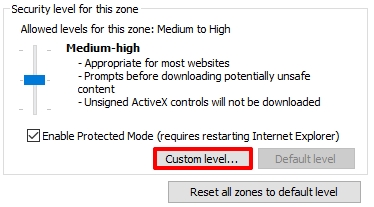
Many mobile browsers limit disabling options due to UI restrictions. Consider third-party browsers like Kiwi Browser, which supports extensions such as NoScript, or DuckDuckGo Browser for built-in script blocking.
For users concerned about privacy after disabling JavaScript, consider integrating Proxy-Seller into your browsing setup. The provider offers fast, private SOCKS5 and HTTP(S) proxies, including residential, ISP, datacenter IPv4/IPv6, and mobile proxies. These proxies keep your identity secure while bypassing geo-restrictions.
Proxy-Seller supports multiple protocols and authentication methods, with proxies available worldwide in 220+ countries. Their dashboard is easy to use and offers 24/7 support. Whether you are web scraping, verifying ads, conducting market research, or simply want secure anonymous browsing when JavaScript is disabled, Proxy-Seller helps maintain both functionality and privacy.
There are two ways to verify whether you managed to disable this option or not:
Disabling JavaScript can significantly change how websites behave and look. Here’s what to expect:
| Positive Effects (Speed & Privacy) | Negative Effects (Functionality) |
|---|---|
| Faster page loads: Browsers skip many DOM manipulations and network calls, speeding up page rendering. | Broken functionality: Many websites rely on JavaScript for forms, logins, menus, sliders, and chat widgets. These may stop working or become unusable. |
| Fewer ads and trackers: Scripts powering ads, pop-ups, and trackers like Google Analytics or Facebook Pixel will not run, improving privacy. | Simplified layouts: Script-generated content won’t load, which often means missing parts of pages, especially on modern Single Page Applications (SPAs) built with frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue. |
| Multimedia issues: Features like video players, interactive maps, and dynamic content generally require scripts, which may fail to display properly. |
These changes are a trade-off. Disabling JavaScript enhances speed and privacy but can break site functionality. Be prepared to enable scripts selectively or switch them back on when needed.
If you want control over scripts without fully disabling JavaScript, try these practical options:
By using these tools and techniques, you gain flexible control over JavaScript, balancing privacy and web functionality without fully disabling scripts. This keeps your browsing smoother and safer while accessing necessary web features.
The process of disabling JavaScript takes only a couple of minutes. Keep in mind that this solution can provide not only advantages in the form of faster page loading and the disappearance of annoying ads. Along with this, important elements may disappear on sites, without which it will not be possible to fully work on them. For example, in Bitrix, when JavaScript is disabled, the artist will no longer display the tasks assigned to him.
And now, find out what is WebRTC and how to disable it.
Comments: 0