
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  اردو
اردو  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski Extracting real property information from Zillow can offer perfect analysis for the market and investments. This post aims to discuss scraping Zillow property listings with Python, focusing on essential steps taken and guidelines. This guide will show you how to scrape information from the Zillow website using libraries like requests and lxml.
You’ll learn how to identify and target the right elements on a Zillow listing page to scrape Zillow data Python effectively. Start by choosing the target URL. For example, use a Zillow listing page for Brooklyn, NY. This page contains multiple property listings that you want to extract.
Next, open your browser’s inspect tools (Chrome DevTools or Firefox Developer Tools) to investigate the page’s DOM structure. Use these tools to confirm the elements you’ll scrape. The key data elements on a Zillow listing page and where to find them are:
To find these elements using BeautifulSoup (one of the best Python libraries for web scraping), you’ll use methods like find(), find_all(), or CSS selectors. For example, find_all("li", class_="ListItem-c11n-8–109–3__sc-13rwu5a-0") gets all property listings. Within each listing, use find("span", {"data-test": "property-card-price"}) to get the price.
Note that some Zillow content loads dynamically. You might find certain data is embedded in JSON scripts or loaded via XHR calls. Use the browser’s Network tab to spot API endpoints Zillow uses internally. Understanding these endpoints can give you an alternative way to scrape data from Zillow, bypassing some complexities of the page HTML.
By mastering how to navigate Zillow’s page structure and target data elements, you build a solid foundation to scrape Zillow data Python effectively.
Before we start, ensure you have Python installed on your system. You’ll also need to install the following libraries:
pip install requests
pip install lxmlTo extract data from Zillow, you need to understand the structure of the webpage. Open a property listing page on Zillow and inspect the elements you want to scrape (e.g., property title, rent estimate price, and assessment price).
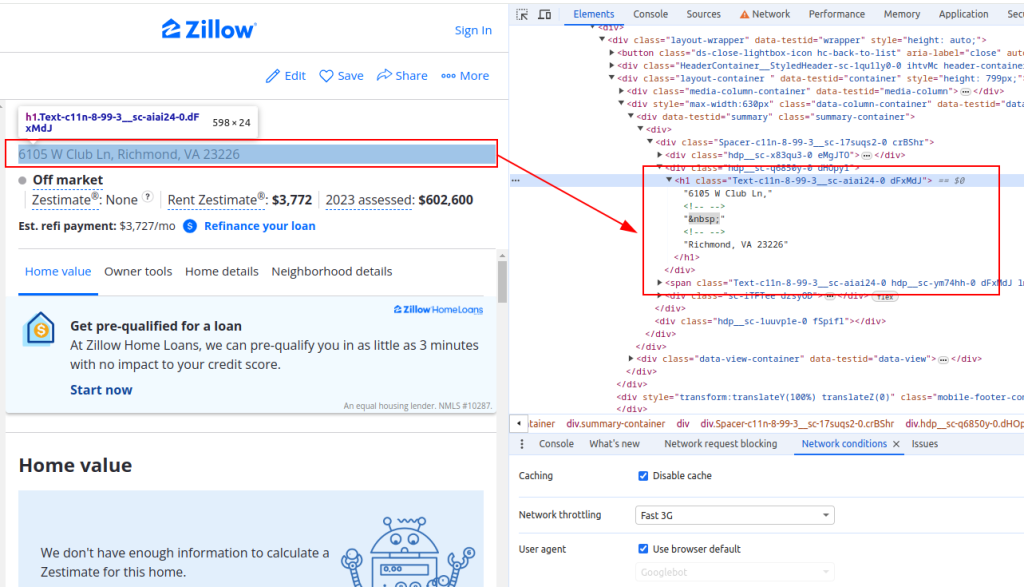
Title:
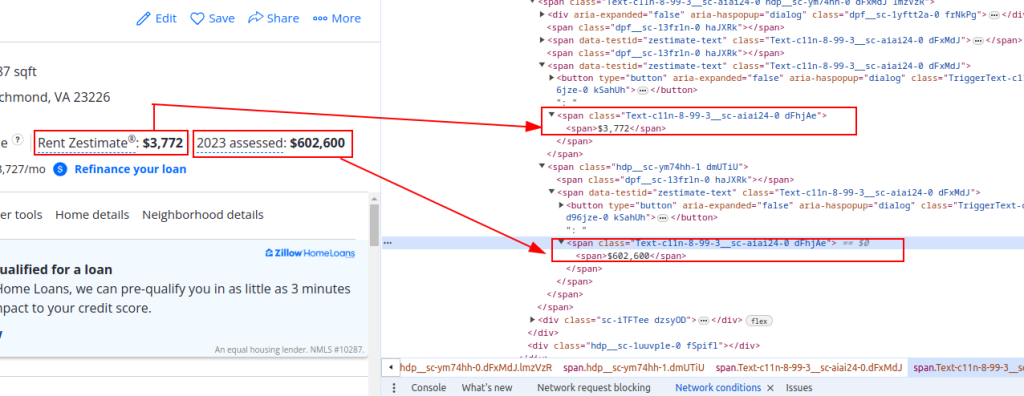
Price Details:
Now let's send HTTP requests. First, we need to fetch the HTML content of the Zillow page. We’ll use the requests library to send an HTTP GET request to the target URL. We will also set up the request headers to mimic a real browser request and use proxies to avoid IP blocking.
import requests
# Define the target URL for the Zillow property listing
url = "https://www.zillow.com/homedetails/1234-Main-St-Some-City-CA-90210/12345678_zpid/"
# Set up the request headers to mimic a browser request
headers = {
'accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7',
'accept-language': 'en-US,en;q=0.9',
'cache-control': 'no-cache',
'dnt': '1',
'pragma': 'no-cache',
'sec-ch-ua': '"Not/A)Brand";v="99", "Google Chrome";v="91", "Chromium";v="91"',
'sec-ch-ua-mobile': '?0',
'sec-fetch-dest': 'document',
'sec-fetch-mode': 'navigate',
'sec-fetch-site': 'same-origin',
'sec-fetch-user': '?1',
'upgrade-insecure-requests': '1',
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36',
}
# Optionally, set up proxies to avoid IP blocking
proxies = {
'http': 'http://username:password@your_proxy_address',
'https://username:password@your_proxy_address',
}
# Send the HTTP GET request with headers and proxies
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
response.raise_for_status() # Ensure we got a valid responseNext, we need to parse the HTML content using lxml. We’ll use the fromstring function from the lxml.html module to parse the HTML content of the webpage into an Element object.
from lxml.html import fromstring
# Parse the HTML content using lxml
parser = fromstring(response.text)Now, we will extract specific data points such as the property title, rent estimate price, and assessment price using XPath queries on the parsed HTML content.
# Extracting the property title using XPath
title = ' '.join(parser.xpath('//h1[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFxMdJ"]/text()'))
# Extracting the property rent estimate price using XPath
rent_estimate_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-2]
# Extracting the property assessment price using XPath
assessment_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-1]
# Store the extracted data in a dictionary
property_data = {
'title': title,
'Rent estimate price': rent_estimate_price,
'Assessment price': assessment_price
}Finally, we will save the extracted data to a JSON file for further processing.
import json
# Define the output JSON file name
output_file = 'zillow_properties.json'
# Open the file in write mode and dump the data
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(all_properties, f, indent=4)
print(f"Scraped data saved to {output_file}")You’ll learn how to download raw HTML content from Zillow correctly and validate it before parsing. Start with the Python requests library. Use requests.get() to fetch the page but include headers that mimic a real browser.
Here is an example:
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br"
}
response = requests.get("https://www.zillow.com/brooklyn-ny/", headers=headers)
Using proper headers helps prevent the site from blocking your scraper or serving bot traps. Always check response.status_code == 200 to confirm a successful request. Also, verify response.encoding and content length to ensure page integrity.
Before parsing, validate that the HTML contains expected keywords or elements. For example, check for "property-card-price" in response.text to confirm that you have the right page content.
For scraping Zillow data python at scale, consider using requests.Session(). This maintains persistent connections and handles cookies automatically, improving scraping efficiency.
Zillow employs IP blocking and rate limiting to defend against scrapers. To overcome these, use high-quality proxies. Proxy-Seller offers fast private SOCKS5 and HTTPS proxies with various authentication methods, perfect for web scraping tasks like scrape data from Zillow.
Proxy-Seller provides multiple proxy types:
They also offer rotation features that help maintain anonymity and avoid IP bans.
Using Proxy-Seller’s proxies enables consistent access to Zillow pages without triggering anti-bot defenses. This helps your scraper reliably download raw HTML content for data extraction.
Keep Proxy-Seller in mind when building your scraping infrastructure to improve reliability and scalability while you scrape Zillow data Python.
You’ll learn how to parse downloaded HTML and extract property details using BeautifulSoup.
Begin by creating a BeautifulSoup object from the response content. Use either the "lxml" or "html.parser" parser for best results:
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml")Next, find all property listings by locating their <li> elements via the class name:
listings = soup.find_all("li", class_="ListItem-c11n-8–109–3__sc-13rwu5a-0")Loop through each listing to extract key data points. Here's how to handle each element:
Use try-except blocks for each extraction step to handle missing elements gracefully. Assign None if an element is not found.
Store each extracted property in a dictionary with keys: price, size, and address. Append each dictionary to a list for later use.
Here is an example of processing each listing:
properties = []
for listing in listings:
try:
price = listing.find("span", {"data-test": "property-card-price"}).text.strip()
price = price.replace("$", "").replace(",", "")
except:
price = None
try:
size_ul = listing.find("ul", class_="StyledPropertyCardHomeDetailsList-c11n-8–109–3__sc-1j0som5-0")
size = size_ul.find_all("li")[-1].text.strip()
except:
size = None
try:
address = listing.find("address").text.strip()
except:
address = None
properties.append({"price": price, "size": size, "address": address})
After extraction, validate and optionally convert data types (e.g., price to int). Log extraction errors for debugging.
In the end, you get a clean list of property dictionaries, ready for analysis or storage. This practical approach teaches you exactly how to scrape data from Zillow using Python and BeautifulSoup.
To scrape multiple property listings, we will iterate over a list of URLs and repeat the data extraction process for each one.
# List of URLs to scrape
urls = [
"https://www.zillow.com/homedetails/1234-Main-St-Some-City-CA-90210/12345678_zpid/",
"https://www.zillow.com/homedetails/5678-Another-St-Some-City-CA-90210/87654321_zpid/"
]
# List to store data for all properties
all_properties = []
for url in urls:
# Send the HTTP GET request with headers and proxies
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
response.raise_for_status() # Ensure we got a valid response
# Parse the HTML content using lxml
parser = fromstring(response.text)
# Extract data using XPath
title = ' '.join(parser.xpath('//h1[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFxMdJ"]/text()'))
rent_estimate_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-2]
assessment_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-1]
# Store the extracted data in a dictionary
property_data = {
'title': title,
'Rent estimate price': rent_estimate_price,
'Assessment price': assessment_price
}
# Append the property data to the list
all_properties.append(property_data)Here is the complete code to scrape Zillow property data and save it to a JSON file:
import requests
from lxml.html import fromstring
import json
# Define the target URLs for Zillow property listings
urls = [
"https://www.zillow.com/homedetails/1234-Main-St-Some-City-CA-90210/12345678_zpid/",
"https://www.zillow.com/homedetails/5678-Another-St-Some-City-CA-90210/87654321_zpid/"
]
# Set up the request headers to mimic a browser request
headers = {
'accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7',
'accept-language': 'en-US,en;q=0.9',
'cache-control': 'no-cache',
'dnt': '1',
'pragma': 'no-cache',
'sec-ch-ua': '"Not/A)Brand";v="99", "Google Chrome";v="91", "Chromium";v="91"',
'sec-ch-ua-mobile': '?0',
'sec-fetch-dest': 'document',
'sec-fetch-mode': 'navigate',
'sec-fetch-site': 'same-origin',
'sec-fetch-user': '?1',
'upgrade-insecure-requests': '1',
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36',
}
# Optionally, set up proxies to avoid IP blocking
proxies = {
'http': 'http://username:password@your_proxy_address',
'https': 'https://username:password@your_proxy_address',
}
# List to store data for all properties
all_properties = []
for url in urls:
try:
# Send the HTTP GET request with headers and proxies
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
response.raise_for_status() # Ensure we got a valid response
# Parse the HTML content using lxml
parser = fromstring(response.text)
# Extract data using XPath
title = ' '.join(parser.xpath('//h1[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFxMdJ"]/text()'))
rent_estimate_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-2]
assessment_price = parser.xpath('//span[@class="Text-c11n-8-99-3__sc-aiai24-0 dFhjAe"]//text()')[-1]
# Store the extracted data in a dictionary
property_data = {
'title': title,
'Rent estimate price': rent_estimate_price,
'Assessment price': assessment_price
}
# Append the property data to the list
all_properties.append(property_data)
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
print(f"HTTP error occurred: {e}")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
# Define the output JSON file name
output_file = 'zillow_properties.json'
# Open the file in write mode and dump the data
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(all_properties, f, indent=4)
print(f"Scraped data saved to {output_file}")By understanding the structure of HTML pages and leveraging powerful libraries such as requests and lxml, you can efficiently extract property details. Employing proxies and rotating User-Agents enables you to make a large volume of requests to sites like Zillow without the risk of being blocked. For these activities, static ISP proxies or rotating residential proxies are considered optimal choices.
Comments: 0