
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski WhatsApp is a widely used social app for smartphones and PCs. It allows users to send text and voice messages, images, and videos, as well as make video calls.
Both the mobile and desktop versions of WhatsApp are working with private proxies, allowing users to bypass regional blocks and add an extra layer of anonymity. Proxies act as intermediaries between the device and WhatsApp servers. When a proxy is set up correctly, the real IP-address is replaced with the proxy server's IP address.
The app developers state that WhatsApp doesn't support the use of private proxies. Instead, users can use public proxy servers running on ports 80, 443, or 5222. However, internet connections through these ports may not always work. Considering these limitations, it's advisable to configure a proxy for the entire system rather than specifically for WhatsApp traffic. For stable and properly configured connections, you can refer to a Whatsapp proxy that supports ports and authentication compatible with the app. For detailed instructions, refer to the guide below:
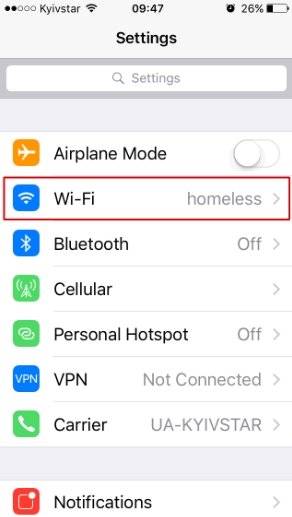
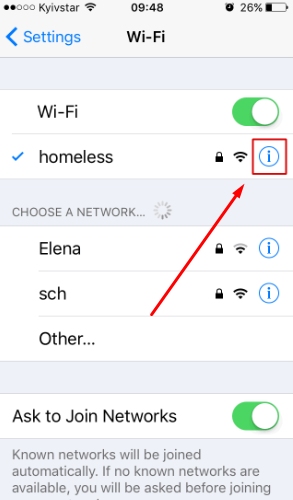
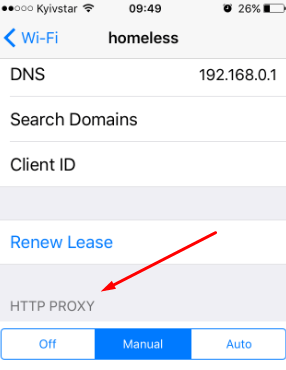
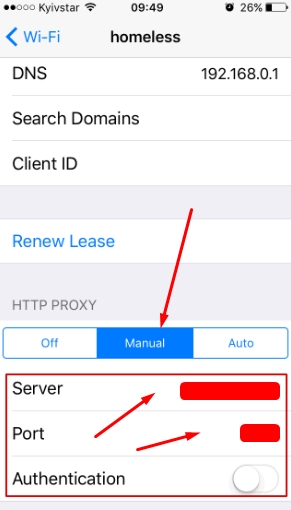
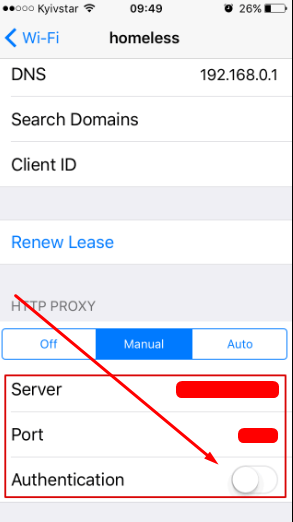
To ensure the proxy is working, restart WhatsApp and try to download or send a file or message. The same iOS system-level approach works for other messengers as well. For users managing multiple social platforms, dedicated proxy solutions — such as WeChat proxy, Tinder proxy, or Snapchat proxy - help maintain stable connections and consistent account performance.
Recent versions of WhatsApp offer options to set up a proxy server inside the application, but their effectiveness is uncertain. In this guide, we will configure the proxy server at the Android device level, allowing all application browsers, including WhatsApp, to use a private proxy.
It's important to note that private proxies do not function when connected to mobile networks. It's necessary to switch to “Wi-Fi”. If you intend to use mobile Internet, consider purchasing mobile proxy LTE specifically for WhatsApp on Android.

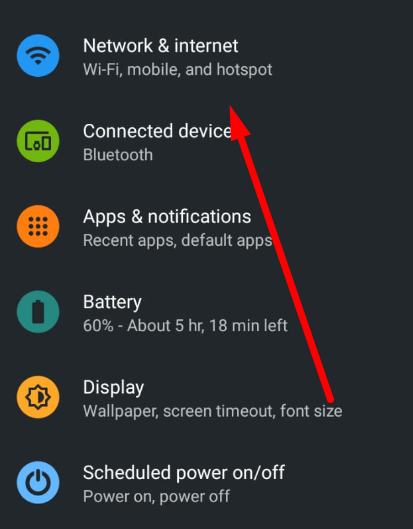
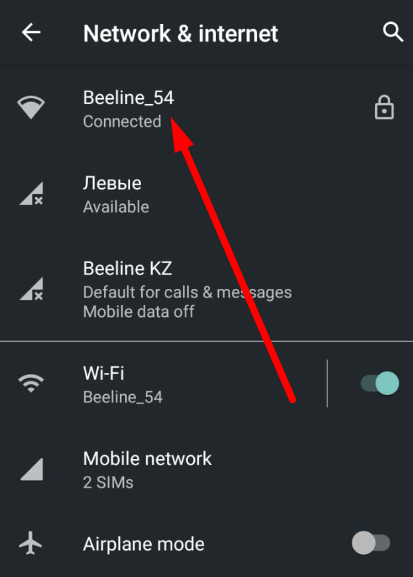
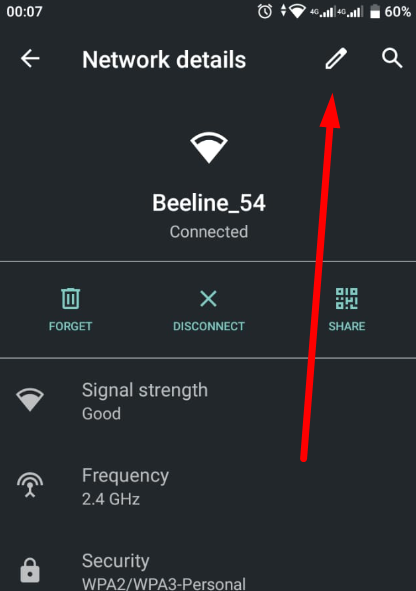
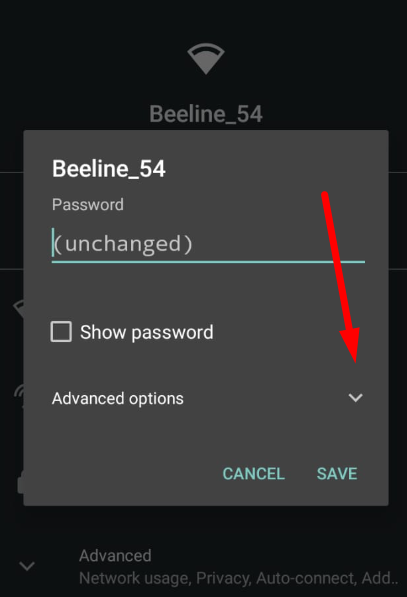
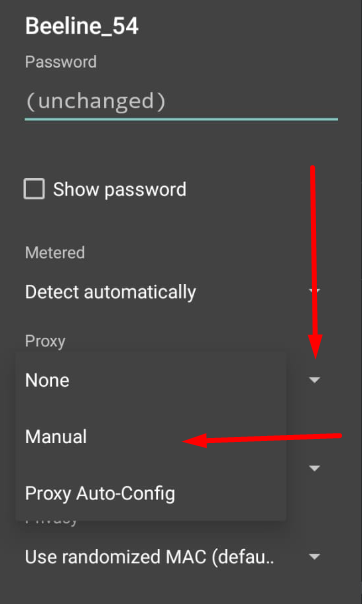
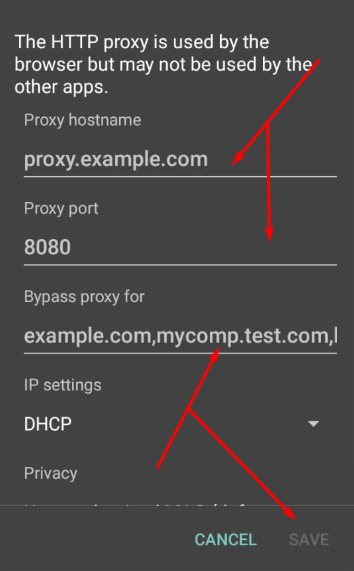
For WhatsApp on Android and iOS, ISP proxy is the optimal choice, as it provides a stable static IP and supports long sessions without frequent reconnects. As an alternative, residential proxy with sticky sessions can be used, while mobile and datacenter proxies are not recommended for continuous WhatsApp use.
Your internet traffic will now be routed through a private proxy IP. To set up proxy servers in WhatsApp with login and password authorization specifically for the application, rather than for the entire system, you can use other applications like Drony.
Comments: 1