
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski For automated interaction with a browser, application testing, web scraping, or executing tasks via scripts, Puppeteer and Selenium are the go-to tools. While both frameworks compete in terms of their capabilities to perform tasks on web resources, they have distinct features that show operational subtleties. Understanding the pros and cons of each tool is essential for determining which one to select for a specific task. This article attempts to outline these differences in a guide to Puppeteer vs Selenium so that you can choose intelligently based on your goals.
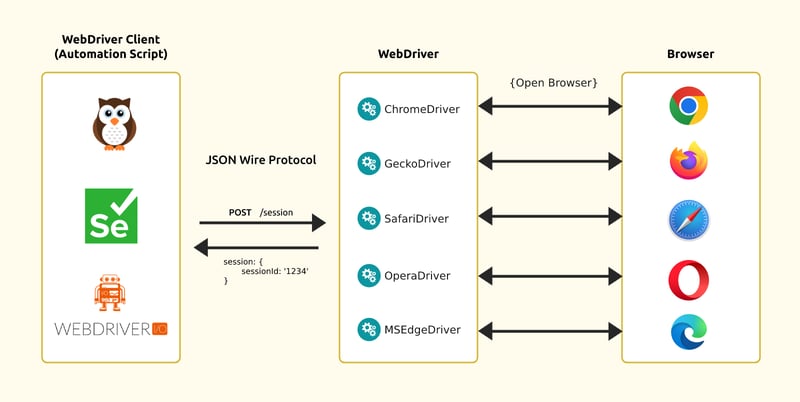
An open-source product provided for free, Selenium is dedicated to automation for browser control, website tests, and data extraction.
The suite components WebDriver, IDE, Remote Control, Grid, and Server have differences in their implementation but all share the same outcome. They simulate user actions in the browser based on an algorithm provided to them.
The following requirements need to be fulfilled for using the browser:
The conditions specified above need to be satisfied to enable the following management algorithm:
Write code in a compatible programming language. ⇒ Run the code. ⇒ The code accesses the Driver. ⇒ The Driver delegates authority to WebDriver (ChromeDriver, FirefoxDriver, etc.). ⇒ WebDriver translates the code into commands and dictates actions. ⇒ The browser processes the request and returns the response.
These operations are required to complete the steps under:
From our observation, this tool enables interaction with any website and offers the ability to test its content, along with interacting with the page components and data extraction, which proves to be especially useful for scraping information that loads dynamically. These are the advantages of Selenium tools that make them preferable in certain areas.
When comparing Selenium vs Puppeteer, Selenium stands out for its broad browser and platform compatibility. Selenium supports Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and even Internet Explorer. It works across Windows, macOS, and Linux, giving you flexibility on nearly any system.
Selenium’s core components include:
For more advanced testing, Selenium offers:
Selenium also adds cutting-edge features:
Beyond features, the Selenium ecosystem is strong. It integrates with popular test frameworks like JUnit, TestNG, PyTest, Mocha, and Jasmine. This helps you build robust test suites quickly. Plus, it fits well into CI/CD pipelines on Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and others to automate testing during development. You’ll also find a rich open-source community offering documentation, plugins, and tools like Allure Reports, Extent Reports, BrowserStack, and Sauce Labs to enhance your testing experience.
Puppeteer is a JavaScript library designed to control Chrome and Firefox browsers. You’ll use it to automate browsing actions like navigation, clicking buttons, and filling out forms with ease. By default, Puppeteer runs in headless mode – you won’t see a browser window, which speeds up tasks like web scraping and routine browser automation.
Key capabilities:
To get the most reliable results, especially for web scraping or large-scale automation, you need dependable proxies. Using fast and secure proxies helps you rotate IP addresses, avoid getting banned, and keep your tasks running smoothly. Proxy-Seller offers proxies optimized for these uses, making your Puppeteer automation faster, safer, and more efficient.
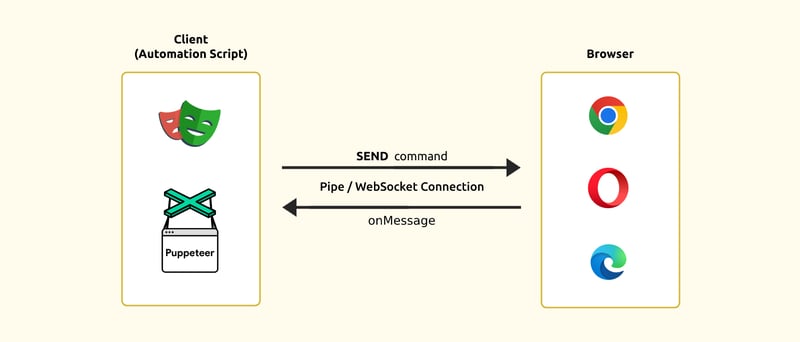
It is a relatively new library for controlling headless Google Chrome browsers remotely. It leverages the high-level API of Node.js and the DevTools protocol for the automation of specific activities.
This library can be interacted with using a command line terminal and knowledge of JavaScript’s basic grammar.
As is the case with the first tool, a few simple steps are required to launch it:
If all settings were performed correctly, interaction with the browser will be structured according to the following scenario:
The library accesses the DevTools Protocol. ⇒ The protocol goes through WebSocket to the browser. ⇒ The browser receives and processes the command. ⇒ Returns the response.
As we see, scenarios of interaction vary for Puppeteer and Selenium. While the first one requires a development environment and WebDriver which interacts via its GUI, the second one is started with the Node package and commands Google Chrome using the JavaScript DevTools Protocol.
This style of the browser’s control works particularly well with AJAX-driven websites because many tools often fail to work with dynamically changing content.
Some of the advantages include:
These sets of capabilities are far from exhaustive. The limitations of the tool are imposed by running in headless mode through the DevTools protocol and WebSocket connection, which allows external testing or automation tools to dispatch commands and receive information from Chrome.
As we pointed out, Puppeteer’s primary limitation is that it only works with Google Chrome, whereas Selenium can be used with various others. This is one of the most important differentiating factors among others.
Let’s take a step further and consider other evaluation criteria and present them in the table “Selenium vs Puppeteer” given below.
| Characteristic | Selenium | Puppeteer |
|---|---|---|
| OS Support | Windows, Linux, macOS | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Programming Language Support | Java, Python, Ruby, C#, JavaScript, Kotlin and others | JavaScript |
| Installation | Development environment, driver for each browser, additional libraries | Node.js and package manager |
| Management | WebDriver | Chrome DevTools Protocol |
| Performance | High RAM and CPU usage, as it operates with interfaces | Minimal RAM and CPU usage, operates in headless mode |
| Testing Platforms | Web and mobile | Web |
| Integration | Compatible with other testing and scraping tools and libraries | Compatibility limited to tools for Google Chrome |
| Documentation | Tutorials, support service, and forum | Tutorials, unofficial forums |
| Types of Testing | Cross-platform, Functional, Performance, UI Testing, Integration | Functional, Performance, UI Testing |
| Scraping | Text, HTML attributes, form data, dynamic content data, links, images | Text + PDF, HTML attributes, form data, dynamic content data, links, images, and media |
From the parameters provided in the table, it is clear that there is some form of compatibility between the tools, but it also shows that they may not be equally effective for every task.
You’ll notice a key difference when examining cross-browser support in the Puppeteer vs Selenium debate.
| Framework | Desktop Browser Support | Mobile/Other Support | Key Limitation/Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Puppeteer | Natively supports Chrome and Firefox. | Limited Safari and mobile browser testing (experimental via CDP/BiDi). | Works best with desktop Chrome/Firefox; support for other platforms is less reliable. |
| Selenium | Supports Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer fully. | Enables mobile browser automation via Appium (Android and iOS devices). | Provides extensive coverage and regularly updates drivers for backward compatibility. |
Selenium’s compatibility with cloud testing platforms like BrowserStack and Sauce Labs is another advantage. These services provide scalable cross-browser testing on real devices and multiple browser versions. This means you can test your applications widely without managing a large infrastructure.
Using proxies plays a critical role in cross-browser and multi-location testing workflows. Proxy services like Proxy-Seller ensure you have stable IPs, helping you avoid geo-restrictions and bans. This improves anonymity and ensures that tests run smoothly across different browsers and regions, a must-have for large-scale Selenium vs Puppeteer for web scraping or automation projects.
In this section, we focus on which is better Selenium or Puppeteer in terms of the speed of operation, which is a basic distinguishing factor between the two tools. This becomes particularly important when working with large datasets or scraping JavaScript-heavy websites.
Let us analyze the performance from a few more angles.
This parameter has to do with how the tool interfaces with the browser.
Selenium, as we noted earlier, uses a WebDriver, which controls the environment over its UI, meaning it adds an extra layer that inflates the time required to get the program running.
So, what are the main advantages of using Puppeteer over Selenium? If using the first one, there is no middleman between the browser and itself, as the connection is done through the DevTools protocol, so the speed of launching becomes much higher compared to the second one.
In the case of WebDriver, the interaction with DOM is done through a client-server model; in this case, Selenium WebDriver serves as the client while ChromeDriver acts as the server. The processing time for this model is determined by the type of driver used as well as the tree structure. The processing time for DOM is higher if the page is served in JavaScript.
With regard to Chromium-based browsers, Puppeteer performs better DOM manipulations due to some distinct features like direct implementation of the DevTools Protocol, a command-based communication model, and the absence of WebDriver as the middleman. Additionally, it cannot be used in conjunction with other ones, making the comparison somewhat biased.
Such a tool like Selenium implements scripting through a dedicated interface using JSON. Each command is issued in JSON format and sent to the appropriate driver (e.g., SafariDriver) via HTTP. The command is executed, and the results are JSON-encoded responses. Selenium’s ManagedWebDriver uses HTTP, which is a partial duplex protocol, thus limiting the speed at which commands can be sent and executed.
Through Puppeteer, it is connected via WebSocket, creating an area of two-way data exchange between the client and the browser. It runs on TCP, a reliable and fast stream of data that is encrypted and authenticated. This protects the information from unlawful access.
Estimates of rendering time in Puppeteer are significantly less than in Selenium. The first simply works with Chromium, while the latter uses additional libraries to keep track of rendering time.
Puppeteer vs Selenium are somewhat comparable in respect of web scraping. The main difference is that with the second one, the choice depends on the particular requirements at hand.
Puppeteer is recommended for:
Selenium applies for:
For deeper parsing in both tools, XPath, CSS selectors, and other methods can be used, which allow for precisely locating the needed tools on the page.
When a comparison is done using Python, it is essential to point out differences in libraries, syntax, and the integration with system design because they change how one's approach with Python and these two tools changes. Let us see what each does with Python.
As it was discussed in earlier topics, Selenium Python proxy allows setting it up from where the resources are sourced. This works well for testing websites and scraping them when there are restrictions using proxy servers.
The official Python library for Selenium is further supported by updates with additional features and additional areas of application. In this case, let us take a look at the example of installing it and starting a browser using WebDriver.
To install it in the development environment, input the command:
pip install seleniumNext, you need to get WebDriver that corresponds to the version of your installed browser:
from selenium import webdriver
# Create a browser object, change the path to your web driver in the code
driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='/path/to/chromedriver')In order to start and go to a site where an element can be found, the commands “get” and “findElement” can be used.
# Open the site
driver.get('https://example.com')
# Extract text from an element
element = driver.find_element_by_tag_name('h1')
print(element.text)
# Close the browser
driver.quit()As we can observe, in Selenium a synchronous approach is implemented; that is, the entire code is executed linearly. This is convenient when performing error detection.
There exist no corresponding official libraries in Python. There is a wrapper that bears the same name, which can be installed with the subsequent command:
npm install puppeteerFurthermore, the tool downloads Chromium automatically, which eliminates the need for installing separate drivers.
You can run the following code to start the app and fetch an image:
//adding library
const pt = require('puppeteer');
pt.launch().then(async browser => {
//browser new page
const p = await browser.newPage();
//set viewpoint of browser page
await p.setViewport({ width: 1000, height: 500 })
//launch URL
await p.goto('https://proxy-seller.com')
//capture screenshot
await p.screenshot({
path: 'proxy-seller.png'
});
//browser close
await browser.close()
})Once again, there are fewer lines of code to achieve the same results, making Python very accessible when performing asynchronous operations. The need for an official library in addition to other pointers can severely hamper users without programming skills.
When selecting a tool for automation, it is worth analyzing both Puppeteer vs Selenium. Both tools have numerous functionalities relevant to the automation of web browsers. However, some specific functionalities may tilt the choice in favor of one of the tools.
Reflecting on its functionalities, it is important to analyze the case of Selenium, which works with Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Opera and Safari. This particular feature makes it the best tool for cross-browser tests and work in specific environments, like testing on different operating systems (macOS Safari).
Selenium’s weaknesses are exposed in worrying situations like those when browser executors are used. Puppeteer is best for Google Chrome with experimental support for Mozilla Firefox; this, however, poses limits to projects that need broad multi-browser support.
Headless, or “headless mode,” refers to running the browser without a graphic user interface aimed at enhancing performance and system resources. Both tools are able to run in headless mode, but the implementation differs.
With Selenium, executing test scenarios is much slower when the graphic user interface is on. However, faster execution is anticipated when the headless mode flag is set with the --headless option.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
options = Options()
options.add_argument('--headless') # Enable headless modeIn this case, only Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge are available. Still, they perform cross-browser and functional tests, filling out forms, and scraping data proficiently.
Likewise, Puppeteer is largely designed to operate in headless mode. And it is by default turned on. To check this in the code, the parameter “headless” has to be set to “true”.
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({ headless: true }); // Headless mode is enabled by defaultThis tool takes screenshots and videos of the user's interactions with the site, as well as browsing JavaScript-heavy pages and numerous server-side engagements. This is helpful in debugging, reporting, or even analyzing a user's movements online.
Puppeteer can also be integrated with CI/CD systems so that the scripts and data scraping operations can be done on the server automatically. If the issue is gathering information without revealing your real IP address, then learning how to set a proxy in Puppeteer will resolve this issue.
Selenium also provides a means of dealing with dynamic content using the execute_script() command.
WebDriver gives this command over to the browser using standard APIs. Here, it is passed to ChromeDriver or GeckoDriver and other associated drivers and is executed at the end of the code.
What could result in the delay of executing code?
While dealing with asynchronous Javascript in a page, if it is being used with Selenium, chances are that Selenium does not have real-time visibility to changes that are happening in the page during its load due to some delay in actual rendering changes. Explicit waits in this case will be useful to wait until the changes are done and the content is ready for interaction; for example, WebDriverWait.
Outside of JavaScript, Selenium performs work with HTML and CSS executed to the document object model or DOM. Selenium interacts with elements in the DOM via ID (findelementbyid()), name (findelementbyname()), Xpath (findelementby_xpath()), and they are able to perform clicks, type into forms and fields, and extract data (text, image, file, link).
The one major disadvantage this tool has in regard to JS and DOM is that it is, unfortunately, bound to the driver, which will have some limitations in how some apps' features can be accessed.
When dealing with JS, Puppeteer uses the page.evaluate() command, which executes arbitrary JavaScript right inside the context of the browser.
For working with the DOM, it has methods such as page.$() and page.(). These methods enable locating features on the page, editing them, retrieving information, and handling text, forms, and fields. At the same time, the interaction with the DOM is direct, without an extra driver.
When evaluating the functionality and convenience of these tools, such as Selenium and Puppeteer, their strengths and weaknesses can be defined.
Selenium advantages and disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of this tool is the reliance on WebDriver, which negatively impacts the performance of scenario execution.
Puppeteer pros and cons:
The drawback of using this library is the limited browser support, which decreases the scope of possible assignments significantly.
Along with other programming tools, Selenium and Puppeteer are valued by AQA specialists, DevOps, Web scraping experts, and SEO specialists.
In order to achieve the desired results, it is crucial to evaluate considerations such as project type, compatibility, responsiveness, and dynamic content working capabilities, to name a few.
If your task includes complex test scenarios that need to be undertaken over multiple platforms and browsers, clearly Selenium would be the preferred option. It is compatible with a large number of them and offers greater freedom concerning the choice of programming language.
Puppeteer has more focus on Chrome and Chromium. It is especially powerful in handling dynamic content and JavaScript execution. Web scraping, working with AJAX and SPA applications, and quick test execution on Chrome can all be handled by this tool. It is optimized for Windows and instability-free during headless mode due to direct interaction with the DevTools Protocol.
Comments: 0