
 en
en  Español
Español  中國人
中國人  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  Deutsch
Deutsch  Українська
Українська  Português
Português  Français
Français  भारतीय
भारतीय  Türkçe
Türkçe  한국인
한국인  Italiano
Italiano  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  اردو
اردو  Indonesia
Indonesia  Polski
Polski Modern society requires sophisticated solutions to ensure privacy, security, and performance. Recognizing what is the difference between proxy and VPN is valuable for individuals or specialists using the Internet. While both technologies, indeed, serve the purpose of obscuring the user identity and obtaining the no access content, they take opposite approaches and have different uses.
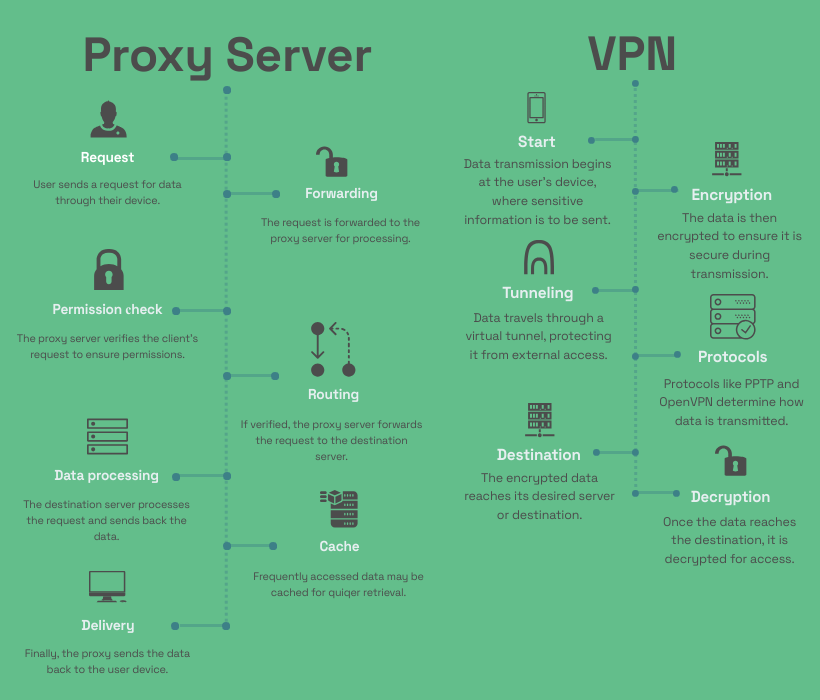
Let’s start off with a main question: is a proxy the same as a VPN? In a broader sense, a proxy server is one of the intermediate systems between a user’s computer and the internet at all. It enables one to issue requests for resources, say, web pages or files which are on other servers. So, a request is issued and forwarded from the computer to the proxy server which further issues the request to the other server and fetches back the required content. This technique aids in masking the IP address of the user. Hence, it ensures a some level of anonymity and also helps in surpassing the geographical limitations.
VPNs, however, cloak your entire internet connection. This means that not only is your IP address hidden, but all other data you send or receive is protected from prying eyes. Notably, VPNs are advantageous for covering sensitive data while using public Wi-Fi networks.
To further understand these tools, we'll explore the residential proxy vs VPN as well as reverse proxy vs VPN differences. Residential proxies use real residential IP addresses, providing high anonymity and fewer blockades during automated tasks and geo-targeting operations. Conversely, VPNs encrypt internet traffic, offering comprehensive security and privacy across all activities online.
So now we are going to take a comprehensive look at the core functions of these both VPN and proxy technologies.
Proxy servers can be defined as a platform that operates in between users and the internet while providing distinctive ratios of protection, privacy and functionality based on the type of proxy server in use or the configuration set up for it. Proxy servers operate through multiple protocols as well as serve different purposes including the following:
Beyond these basic types, proxies can be categorized by source and method of operations:
From enhancing security to hiding identities such as managing multiple proxies, each kind of proxy offers specific benefits designed for the intended objectives and situations.
Let’s compare proxy server vs VPN deeply. When it comes to VPNs, the entire connection to the internet will be encrypted making the transfer of data entirely secure from any cyber threat. This offers great capture of sensitive information especially when the information is on a public network.
Proxies on the other hand only focus on changing the IP address by rerouting the requests, and not encrypting any data. Proxies are mainly suitable for those users who want quick access to restricted websites without needing much security.VPNs, and Proxy servers vary in the manner they preserve one’s privacy and security.
While VPNs assist in blocking all internet traffic on the device, focusing on maintaining a simplified security for all applications, proxies sometimes require configurations by application settings. Furthermore, proxies are preferred over VPNs for tasks that are speed sensitive and don’t deal with sensitive information since VPNs tend to slow down connections more.
Understanding these differences is key to answering the question, “what is better, a VPN or proxy server?” as it helps clarify which option might be better suited for specific online activities.
The choice between a VPN and a proxy is dependent on factors such as the data security the users require and the type of content the users seek. VPNs account for the total length of a data path which, when employing the transmission media, renders them advantageous for total data protection. For this reason, they are very useful to users on unreliable networks or those that work with confidential information.
While it is true that proxies do not offer data encryption, they are great for IP masking for geo-blocking. This enables faster access to regionized content. This can be especially useful in situations like when a user is in a different region and needs access without the communication having to be encrypted. So, while VPNs are ideal for complete online activity protection, proxies cater to users who require ease of access and limited geographical presence rather than extensive data security.
Thus, the answer to the question of what is better, VPN or proxy, depends on whether a user values comprehensive protection with VPNs or fast connections with proxies. Both tools excel in their respective areas.
VPNs and proxies together combine the strengths of both technologies, therefore elevating the security and flexibility of users. Here are some detailed examples of scenarios where employing both technologies simultaneously can be particularly beneficial:
Scenario: An analyst has to collect and benchmark prices, or the existence of a product, from websites that contain different information based on the user’s geographic position.
Use case: Using a VPN for personal security and privacy with a proxy to change the region’s IP address allows the analyst to accurately perform necessary online activity without revealing their actual location, and most importantly, without compromising data security.
Scenario: Social media managers need to handle multiple accounts and run regional-specific ad campaigns that appear to originate from the targeted locality.
Use case: The manager logs onto the sensitive account or the online platform using a public or any untrusted network. Doing so leaves their sensitive information open. By using a VPN while logging on, along with using proxies to connect from different geographical positions, the information is hidden. This allows for proper management of localised content and advertisements without revealing the true IP position.
Scenario: Programmers have to examine applications or services that have been created for different regions, to ensure that the application or service is compatible from any place the user may log in from.
Use case: VPNs allow developers to protect their development settings as well as their sensitive documents. In addition, they can use proxies to impersonate users in various locations to check localization, geoblocking, and other multi-region deployment features.
When considering using VPNs vs proxies, or both simultaneously, the information above enables the selective application of each technology based on specific requirements.
Each mentioned tool in this article performs a specific function in interaction online, and knowing these differences is perhaps the most vital aspect when building your digital presence.
Below is the provided comparison list which specifically focuses on the advantages and disadvantages of both technologies, highlighting the proxy and vpn comparison.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Indeed, proxy servers come in handy when there is a need for speedy and targeted access, like streaming media that might be geo-blocked. Nevertheless, sometimes they do not offer the needed security for sensitive operations. But, VPNs are crucial for achieving complete security and privacy, which makes them very useful in business and personal activities where confidentiality is paramount.
Comments: 0